Nafion
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Nafion | ||||||
| other names |
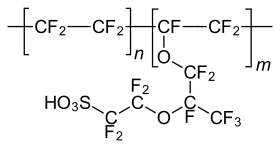
2- [1- [Difluoro [(trifluoroethenyl) oxy] methyl] -1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy] -1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethanesulfonic acid |
||||||
| CAS number | 31175-20-9 | ||||||
| Monomers / partial structures | |||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to pale brown solid |
||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| density |
1.98 g cm −3 |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Nafion is a perfluorinated copolymer that contains a sulfo group as an ionic group . It was developed in the late 1960s by Walther Grot as a modification of Teflon . Nafion is one of the ionomers and is a registered trademark of DuPont .
properties
The strongly acidic sulfonic acid groups in the Nafion enabled a perfluorinated polymer with ionic properties for the first time. It shows some characteristics that differ fundamentally from those of Teflon while maintaining the high chemical resistance:
- rapid diffusion of water and alcohols, but hydraulically tight
- selectively conductive for protons and other cations ( blocking effect for anions)
- high operating temperatures compared to other polymers (up to 190 ° C)
Technical applications for Nafion membranes
- Ion exchangers - membranes in chlor-alkali electrolysis
- Drying or humidification of gases due to its high selectivity and permeability for water (vapor)
- Proton exchange membrane in polymer electrolyte and direct methanol fuel cells
- Production of chromic acid and regeneration of contaminated chromium baths
- Production of potassium dicyanido aurate (I) by dissolving a gold anode in potassium cyanide (KCN)
- As a strongly acidic, solid catalyst
Like other perfluorinated exchange materials, Nafion largely loses its proton conductivity from a temperature of 100 ° C and in direct methanol fuel cells shows too high a permeability for water and methanol.
Web links
- Nafion properties ( Memento from August 1, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- What is Nafion? ( Memento from September 27, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
Trade names
- Nafion (DuPont)
- Flemion (Asahi)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Data sheet Nafion ® NR50 from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 12, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ DuPont Fuel Cells: DuPont Nafion PFSA Membranes , accessed September 22, 2019.
- ↑ Flemion (Fluoropolymer Ion-Exchange Membrane) ( Memento from December 1, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
