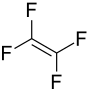
Tetrafluoroethylene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetrafluoroethylene | |||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 F 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
extremely flammable, colorless gas with a sweet odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 100.02 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.51 g l −1 (0 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−142.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−75.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.95 M Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
heavy in water (179 mg l −1 ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
<1 (based on 100 years) |
|||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−658.9 kJ mol −1 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) is a chemical compound from the group of fluoroalkenes and at the same time the simplest fully fluorinated compound .
Extraction and presentation
TFE can be produced by the fluorination of chloroform and subsequent pyrolysis of the chlorodifluoromethane produced.
properties
TFE is not chemically stable; without oxygen it can break down to carbon and tetrafluoromethane , thereby releasing large amounts of energy. It is usually provided with a stabilizer , but the effect of this can be canceled when heated. Its critical temperature is 33.3 ° C, its critical pressure is 40.5 bar, its critical density is 0.58 g · cm −3 , its triple point temperature is −131.25 ° C and its triple point pressure is 0.01168 bar .
use
Tetrafluoroethylene is used to produce polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and as a copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and ethylene .
In refrigeration technology, it is the subject of current research as a refrigerant due to its low global warming potential and is a candidate for use in mixtures primarily with difluoromethane or R32, since decomposition reactions occurred in tests as a pure substance. It would be used as a replacement for pure R32 in refrigeration equipment from mainly Japanese manufacturers.
safety instructions
Tetrafluoroethylene is classified as carcinogenic category 2 (substances that are to be regarded as carcinogenic for humans).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on tetrafluoroethene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 17, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-21.
- ↑ Dae Jin Sung, Dong Ju Moon, Yong Jun Lee, Suk-In Hong: Catalytic Pyrolysis of Difluorochloromethane to Produce Tetrafluoroethylene. In: International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering. 2, 2004, doi : 10.2202 / 1542-6580.1065 .
- ^ Hashimoto, M .: Development of New Low-GWP Refrigerants-Refrigerant Mixtures Including HFO-1123 . In: Science and Technology for the Built Environment . tape 25 . Taylor & Francis, 2019, pp. 776-783 .
- ↑ National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences , 13th Report on Carcinogens (RoC): Tetrafluoroethylene , accessed November 18, 2014.




