Nasal cavity
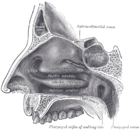
The paired nasal cavity ( Cavitas nasi ) is part of the respiratory tract and contains the organ of smell . The nasal septum ( septum nasi ) separates the left and right nasal cavities, in which a nasal vestibule located inside the outer nose ( vestibulum nasi ) and, deeper, the actual nasal cavity ( cavum nasi proprium ) can be distinguished. The cavum nasi, lined by a mucous membrane with ciliated epithelium , is subdivided into the nasal passages ( meatus nasi ) in layers between the floor and roof of the nasal cavity by bony-supported turbinates ( conchae nasales ) . The median wall forms the septum; in the side wall there are entrances to the paranasal sinuses . The nasal cavities open towards the rear via the choanae to the nasal part of the pharynx.
In humans, three turbinates can usually be distinguished:
- Upper turbinate ( Concha nasalis superior , in animals Concha nasalis dorsalis )
- Middle turbinate ( Concha nasalis media )
- Inferior turbinate ( Concha nasalis inferior , in animals Concha nasalis ventralis )
Occasionally, an uppermost turbinate concha nasalis suprema can also be formed.
The turbinates delimit three nasal passages:
- Upper nasal passage ( Meatus nasi superior , in animals Meatus nasi dorsalis ): between the upper and middle turbinate. With non-primates, it ends blind. The olfactory organ ( organum olfactorium ) is located in the back of this duct , which is why the duct is also called the olfactory duct .
- Middle nasal passage ( Meatus nasi medius ): between the lower and middle turbinate. The middle nasal passage also ends blind in non-primates. The paranasal sinuses ( sinus paranasales ) are connected to it, therefore also called the sinus duct .
- lower nasal passage ( meatus nasi inferior , in animals meatus nasi ventralis ): between the palate and the inferior turbinate. It leads via the choan opening into the nasopharynx and serves as an airway, therefore also known as the airway . In the front part opens nasolacrimal passage ( nasolacrimal duct ) with a fold of mucous membrane ( Hasner-flap ).
In primates , including humans, all three nasal passages lead via the choanic opening into the nasopharynx and serve as an airway. Compared to non-primates, the nose is shortened and significantly higher, the turbinates are reduced and simpler in shape.
Sagittal section, lateral view of the side wall (in the direction of the maxillary sinus )
Sagittal section with the conchae removed
literature
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: respiratory system . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon, Hans Geyer, Uwe Gille (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine . 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 324-367 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Jochen Fanghänel, Franz Pera, Friedrich Anderhuber, Robert Nitsch (eds.): A. Waldeyer - Anatomie des Menschen. 17th, completely revised edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin et al. 2003, ISBN 3-11-016561-9 , p. 316 .