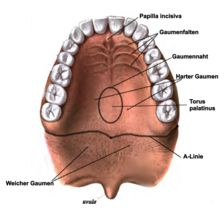
palate

1 incisive papilla , 2 hard palates, 3 palatal palate, 4 palatal suture, 5 soft palate , 6 soft palate almond
The palate ( Latin palatum ) is the upper wall or the ceiling of the oral cavity in the higher vertebrates , whereby this is separated from the nasal cavity and in mammals partly also from the throat . The roof of the mouth is an abutment for the tongue and is therefore of great importance when eating and speaking.
Bony foundation
The actual or hard palate is formed by the bone plates, extending from the upper jaw extending into the depth of the oral cavity and of the horizontal parts of both the maxillary ( Processus palatini ) and palate legs ( laminae horizontal ), so of four, by seams joined together bone parts consist.
Hard palate
The hard palate ( Latin palatum durum ) is covered by a well-perfused (dense venous plexus ), glandular mucous membrane , which in animals mostly has pigmented areas. The palatal mucosa merges into the gums in front and on the sides .
The mucous membrane of the palate has transverse ridges, the palatal stalks ( Latin rugae palatine ). In the midline, the line of adhesion of the palatal processes that fuse during the embryonic palate formation is more or less clearly visible as a palatal suture ( raphe palati in Latin ), even in adults . If this fusion does not take place, a cleft palate ( palatoschisis ) develops , which is often associated with the formation of a gap in the lip and jaw (see cleft lip and palate )
At the front end of the palate there is a small elevation, the incisive papilla , on which the incisive duct opens. The blood supply is mainly via the descending palatal artery . The back two thirds are innervated by the greater palatine nerve.
In the case of fish , amphibians , snakes and lizards , teeth can also be attached here , the number and position of which is important for systematic zoology .
Soft palate
Towards the throat, the hard palate in mammals continues into the soft palate ( Latin velum palatinum or soft palate, Latin palatum molle ). Two folds of the mucous membrane extend from the soft palate and lead to the base of the tongue and the lateral wall of the pharynx. They are called the palatal arches . In the middle of the soft palate is in humans, the uvula (uvula) .
literature
- F.-V. Salomon et al. (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine . 2nd ext. Edition. Enke-Verlag Stuttgart, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1