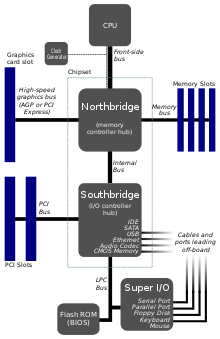
Northbridge
The Northbridge ( German " north bridge " ) refers to a hardware component of a modern PC - motherboard . Traditionally, the Northbridge is a separate chip that, unlike the Southbridge, is located close to the CPU in order to be able to transfer data quickly. The two chips (north and south bridge) are collectively referred to as the chipset . However, there is no need to provide the northbridge as a separate chip ( recent developments ).
Intel calls some of its Northbridges Memory Controller Hubs ( MCH ). In the case of Nehalem-based processors , the term Uncore describes, among other things, the Northbridge functionality integrated in the processor.
Typical tasks
The task of the northbridge is to synchronize and control broadband data transfers with the lowest possible latency . It is therefore high up in the control hierarchy. B. the main processor with the graphics card , with older mainboards it is also responsible for the data exchange between the main processor and the main memory , but this is no longer common because the main processor and the main memory are directly connected to each other. The other peripheral devices are usually only connected indirectly via a connection to the Southbridge. Due to the high data throughput that a Northbridge usually has to deal with, it must be designed with a corresponding broadband and clocked at high speeds. Therefore, cooling is usually necessary.
Processor bus
Since the processor core must be able to communicate with the rest of the system, there must be a remote station for it that understands the bus protocol and translates and forwards the data transfers. This is one of the most important functions of the northbridge. This connection is usually implemented as a front side bus (FSB), that is, it is designed as a bus in which several processors can also participate. However, there are also developments that use a point-to-point protocol instead of a bus , for example HyperTransport or QPI .
Storage controller
In principle, the Northbridge contains at least one memory controller to control the memory and make it available to the system. Depending on the requirements, these can be multi-channel controllers (e.g. dual-channel controllers ) or other controllers in order to support different memory types (e.g. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM). Often these can only be used exclusively (no mixed equipment).
Connection of the graphics card
Devices are usually connected via the Southbridge, but there is one popular exception: the graphics card. Since the connection to this is usually very broadband, the northbridge usually contains the control logic in the form of an AGP or PCI Express connection or an integrated graphics unit . The PCIe x1 slots are, however, connected by the Southbridge.
Connection to the southbridge
The southbridge is usually used to connect additional devices to the system. The connection between the north and south bridges used to be implemented via the ISA or PCI bus ; later, for speed reasons, proprietary point-to-point connections were used . Since the advent of PCI-Express, it has been used more and more.
Recent developments
Since the 2000s, the northbridge has been on the decline as a separate chip: processors such as the AMD Athlon 64 or the Intel Core i7 already integrate some or all parts of a northbridge for speed reasons, which means that a separate chip is no longer necessary. Although only the southbridge remains of the chipset , this is also called a chipset .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Review: Latest Intel Core i7 Gives New Meaning To 'Extreme'. Retrieved November 19, 2011 .