PStB 6
| PStB 6 | |
|---|---|
|
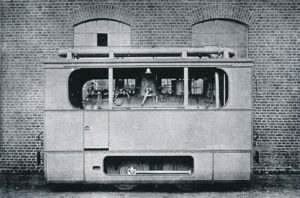
Factory photo
|
|
| Numbering: | PStB 6 |
| Number: | 1 |
| Manufacturer: | Humboldt |
| Year of construction (s): | 1900 |
| Retirement: | 1929 |
| Type : | B n2tk |
| Gauge : | 1000 mm ( meter gauge ) |
| Total wheelbase: | 1,460 mm |
| Service mass: | 18.2 t |
| Friction mass: | 18.2 t |
| Wheel set mass : | 9.1 t |
| Top speed: | 25 km / h |
| Indexed performance : | 59 kW (80 PS) |
| Starting tractive effort: | 25 kN |
| Driving wheel diameter: | 850 mm |
| Control type : | Joy control |
| Cylinder diameter: | 270 mm |
| Piston stroke: | 350 mm |
| Boiler overpressure: | 14 bar |
| Grate area: | 0.60 m² |
| Evaporation heating surface: | 30.4 m² |
| Water supply: | 1.8 m³ |
| Fuel supply: | 0.8 m³ |
| Brake: |
Suction air brake type Körting hand brake |
The PStB 6 locomotive was a tram locomotive made by the Humboldt mechanical engineering institute and was part of a series of three units produced in 1900 for the Meiderich – Neumühl – Dinslaken tram .
Of these three locomotives, the Plettenberg tram received one of the aforementioned locomotives, which was in use until 1929.
History and commitment
Under the designation PStB 6 , the Plettenberg tram received this locomotive used by the Meiderich – Neumühl – Dinslaken tram (number 3 there), which was designated by the manufacturer as a type T 30 tram locomotive . The locomotive comes from a construction lot that also includes the Hohenlimburger Kleinbahn 5 and the locomotive 5 of the Ottensener Industriebahn .
The Plettenberger locomotive was provided for the mixed train service, and with a vacuum brake system Körting equipped. According to the factory, the locomotive is said to have pulled a load of 730 t on the level. In 1929 it was retired.
technology
The locomotive had an inner frame. The cylinders and the controls were arranged inside the frame and acted on the double-cranked rear drive axle. The driver stood to the right of the boiler and could operate the regulator from there. The stoker was at the back of the locomotive. The coal boxes were arranged to the right and left, the water boxes were attached to both ends of the locomotive under the floor. The boiler had two suction injectors of the Strube type and two safety valves.
Via a shuttle valve, the exhaust steam from the machine system could either be conducted directly into the open air or through a condenser; in the latter case, the condensed water was returned to the water tank. This facility was later removed. The locomotive was equipped with a suction air brake, it did not have side buffers.
literature
- Wolf Dietrich Groote: The Plettenberger Kleinbahn . Verlag Kenning, Nordhorn 2002, ISBN 3-933613-56-6 , p. 61 .
Web links
- Website about the Plettenberger Kleinbahn
- Website about the Plettenberger Kleinbahn at www.alt-plettenberg.de
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Wolf Dietrich Groote: The Plettenberger Kleinbahn . Verlag Kenning, Nordhorn 2002, ISBN 3-933613-56-6 , p. 61 .