Pellizzari reaction
The Pellizzari reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry . It was named after the chemist Guido Pellizzari , who published it in 1894. With the help of this reaction, 1,2,4-triazole or corresponding derivatives can be prepared.
Overview
During the reaction, amides (left) react with hydrazides to form 1,2,4-triazoles or their derivatives.
 Overview reaction of the Pellizzari reaction; the radicals R correspond to hydrogen or an organic radical , but do not have to be the same.
Overview reaction of the Pellizzari reaction; the radicals R correspond to hydrogen or an organic radical , but do not have to be the same.
mechanism
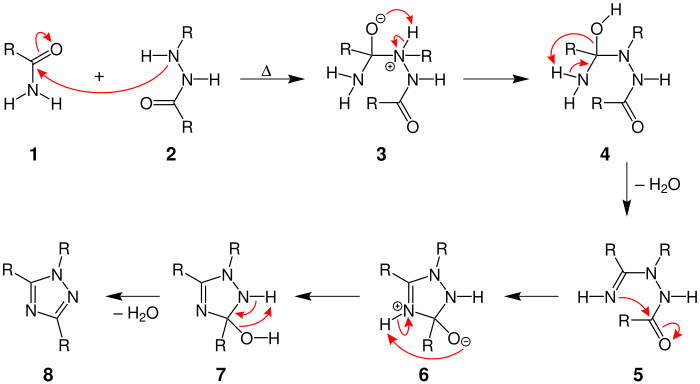 Mechanism of the Pellizzari reaction; the radicals R correspond to hydrogen or an organic radical, which can be identical or different.
Mechanism of the Pellizzari reaction; the radicals R correspond to hydrogen or an organic radical, which can be identical or different.
Initially, the carbon atom of the carbonyl group in amide 1 is attacked by a nitrogen atom in hydrazide 2 . In molecule 3 the hydrogen is split off from the nitrogen and forms a bond with the oxygen atom . By splitting off water from molecule 4 , the nitrogen forms a double bond with carbon 5 (formation of an imine ). This is followed by an intramolecular attack on the carbonyl group, which leads to the formation of a five-membered ring 6 . After another proton migration and the subsequent elimination of water , the 1,2,4-triazole 8 is formed from 7 .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Z. Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. Vol. 2, John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2157-2158.
- ↑ Guido Pellizzari In: Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1911, 41, p. 20.