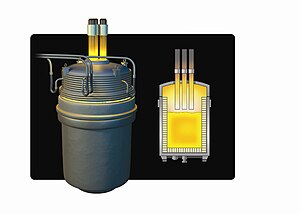
Ladle oven
Ladle furnaces are used in the steel industry. In specialist circles, the LF ( English Ladle Furnace ) is often used . They are used to heat the liquid steel and keep it warm in secondary metallurgy . They are also used to treat liquid steel in order to achieve the correct casting temperature and to be able to set the exact analysis. The ladle furnace is designed as a single- or three-phase electric arc furnace . In addition, the melt is prepared in the ladle furnace for the continuous casters or ingot casting .
This happens among other things through:
- Setting the exact casting temperature to ± 3 K
- Deoxidizing by coiling aluminum wire. This is necessary so that the residual oxygen is bound in the melt and does not combine with other alloys.
- Alloy with FeMn, FeCr, FeSi , ...
- Homogenize the melt by flushing the pan with argon
- The inclusion modification is achieved by adding CaSi to the alloy , whereby CaSi can also be coiled in via wire
Components

Oven transformer for supplying a 3-phase ladle oven with electrical energy
The ladle furnace essentially consists of:
- Electrodes with electrode holders
- transformer
- water-cooled ladle furnace lid with various openings for the electrodes, opening for adding alloy, opening for temperature and sampling, aluminum wire, furnace camera, ...
- Temperature measuring and sampling device
- Alloy addition with vibrating channels and conveyor belts
- Aluminum winding machine, whereby cored wire can also be wound
literature
Wolfgang Bleck: Handbook steel - selection, processing, application . Carl Hanser Verlag, Munich 2018, ISBN 978-3-446-44961-9 , pp. 81 f .