Phillip Island (Norfolk Island)
| Phillip Island | |
|---|---|
| Phillip Island as seen from Norfolk Island | |
| Waters | Tasman Sea |
| Geographical location | 29 ° 7 '14 " S , 167 ° 57' 5" O |
| length | 2.2 km |
| width | 1.9 km |
| surface | 1.9 km² |
| Highest elevation | Jacky Jacky 280 m |
| Residents | uninhabited |
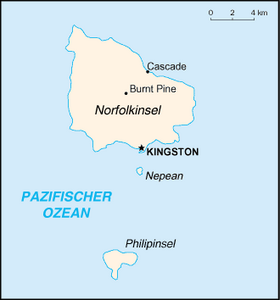
| Map of the Norfolk Island (Phillip in the far south) | |
Phillip Iceland ( German Phillip Island ) is a island and is located in the territory of Norfolk Island , an Australian external territory in the Pacific Ocean . The island is named after Arthur Phillip , the first governor of New South Wales .
The island with 1.9 square kilometers of land is not inhabited. It is located about 6 kilometers off the south coast of the main island with its capital Kingston and about 4.5 kilometers south of the island of Nepean . The island is part of the Norfolk Ridge , a sub-sea ridge that stretches over 1,000 km south of New Caledonia . Jacky Jacky is the highest point at 280 m .
flora
The island's special flora includes some endemic plants, including a species of Malvaceae, Hibiscus insularis Endl. , a critically endangered species, and the grass species Elymus multiflorus subsp. kingianus (Endl.) de Lange & ROGardner . A species of the Fabaceae from the tribe of the Galegeae , Streblorrhiza speciosa Endl. died out in the 19th century.
fauna
Phillip Iceland is a breeding ground for many seabirds like Providence Petrel ( Pterodroma solandri ), Kermadec petrel ( Pterodroma neglecta ) Blackwing Petrel ( Pterodroma nigripennis ), white-naped Petrel ( Pterodroma cervical ), wedge-tailed shearwater ( Puffinus pacificus ), little shearwater ( Puffinus assimilis ), Red-tailed tropicbird ( Phaethon rubicauda ), various frigate ( Fregata ), Australian Coot ( Morus serrator ) Maskentölpel ( Sula dactylatra ) Sooty ( sterna fuscata ), Noddi ( Anous stolidus ) Weißkappennoddi ( Anous minutus ), Graunoddi ( Procelsterna albivitta ) and fairy tern ( Gygis alba ).
There are two reptile species endemic to the islands of the Tasman Sea on the island : the skink Oligosoma lichenigera and the gecko Christinus guentheri . Both species are extinct on Norfolk Island.
literature
- Norfolk Island National Park (Ed.): Norfolk Island National Park and Botanic Garden - Phillip Island . Leaflet with information about flora on Phillip Island. Australian Government - Director of National Parks (English, online [PDF; 508 kB ; accessed on October 13, 2017]).
- Peter Coyne: Incredible! The amazing story of the birth and rebirth of a natural treasure: Phillip Island, South Pacific . Petaurus Press, Belconnen, ACT 2009, ISBN 978-0-9806528-0-2 (English, limited preview in Google book search).
Web links
- The Off-shore Islands. In: The Essential Guide to Norfolk Island. Peter Clarke (English, information about the islands of Nepean and Phillip).
Individual evidence
- ^ The Off-shore Islands. In: The Essential Guide to Norfolk Island. Peter Clarke, accessed October 13, 2017 .
- ^ Phillip Island. What is here? In: Norfolk Island Living Library. Norfolk Island Central School, accessed October 13, 2017 .
- ^ Phillip Island. History. In: Norfolk Island Living Library. Norfolk Island Central School, accessed October 13, 2017 .
- ↑ Elymus multiflorus subsp. kingianus - critically endangered species listing. In: Threatened species. New South Wales Government - Office of Environment & Heritage, accessed October 13, 2017 .
- ^ Phillip Island. Why is it important? In: Norfolk Island Living Library. Norfolk Island Central School, accessed October 13, 2017 .
- ↑ Peter Cochrane (Ed.): Norfolk Island National Park and Norfolk Island Botanic Garden Management Plan 2008 - 2018 . Australian Government –Director of National Parks, 2008, ISBN 978-0-642-55389-8 , A description of Norfolk Island National Park and Norfolk Island Botanic Garden - Conservation significance, p. 3–4 (English, online [PDF; 2.7 MB ; accessed on October 13, 2017]).