Post squirrel
| Post squirrel | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
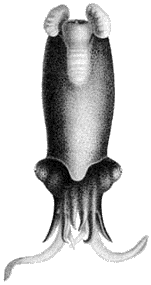
Post squirrel (drawing by Carl Chun ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Spirulidae | ||||||||||||
| Owen , 1836 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Spirula | ||||||||||||
| Lamarck , 1799 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Spirula spirula | ||||||||||||
| ( Linnaeus , 1758) |
The post squirrel ( Spirula spirula ) belongs to the class of cephalopods and within this to the group of cuttlefish (Coleoidea). It is the only representative of a formerly larger order Spirulida still alive today . The oldest representatives of the group are known from the Carboniferous (about 360 to 300 million years ago).
Way of life
During the day, the post squirrel lives at a depth of 550 to 1000 meters. At night, however, it can also be found at shallower depths of at least 100 meters. It follows the swarms of the animal plankton.
casing
The post squirrel has a spiral casing (the phragmocone ) hidden in its coat with non-touching coils, which is why it is called in English ram's horn squid (" ram's horn squid "). The housing has a diameter of 2 to 3 cm and is divided into different chambers in which gas is contained. The gas in the individual chambers can be regulated to a small extent by the animal and keeps the animal in "headstand" floating in the water column. Contrary to popular belief, the housing is not used for ascending or descending the water column. The animal moves quickly with the help of its fins and also up and down in the water column. The post squirrel has ten arms, two of which are designed as tentacles.
The shells of dead animals can occasionally be found en masse on tropical beaches.
Fossil representative

Until recently, the genera Naefia and Groenlandibelus from the Upper Cretaceous were considered to be the oldest representatives of the order. Then, however, new forms from the carbon were found, which, due to their wall structure, can clearly be compared to the Spirulida. However, the group achieved the greatest diversity in the Tertiary . The best known form is Spirulirostra from the Miocene of Europe. You can find them in many clay pits in northern Germany.
Systematics
The cuttlefish system is now widely accepted at family level. In contrast, the classification of the larger groups within the squid is still not stable. In their 2005 monograph, Jereb and Roper lead the post squirrels again as a family within the Sepiida. However, the fossil representatives of the group are not taken into account. In 1922, Naef left a number of families that were to be placed in the line of the post squirrels. From this point of view, a higher hierarchy of the post squirrels is entirely justified.
literature
- Winfried Haas: Trends in the Evolution of the Decabrachia. Berliner Paläobiologische Abhandlungen, 3: 113-129, Berlin 2003. ISSN 1612-0361
- Patrizia Jereb and Clyde FE Roper: Cephalopods of the World - An Annotated and Illustrated Catalog of Cephalopod Species Known to Date. Volume 1 Chambered Nautiluses and Sepioids (Nautilidae, Sepiidae, Sepiolidae, Sepiadariidae, Idiosepiidae and Spirulidae). FAO Species Catalog for Fishery Purposes, No. 4, 1: 1-262, Rome 2005 ISBN 92-5-105383-9
Web links
- Information in English with pictures
- Image from the Science Information Service (idw)
- Spirula spirula inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Endangered Species . Listed by: Barratt, I. & Allcock, L., 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2013.


