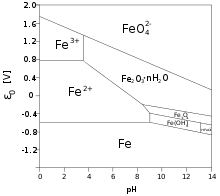
Pourbaix diagram
Pourbaix diagrams (also known as potential-pH diagrams ) graphically represent the areas of thermodynamic stability in metal-electrolyte systems and are used to predict whether or not a metal could corrode.
description
A Cartesian coordinate system is used, with the pH value on the abscissa and the normal potential , which was determined using the Nernst equation, on the ordinate . Usually the diagrams are created for a temperature of 25 ° C and a concentration of 1 mol / l . A distinction is made between three areas: The corrosion area with a proportion of dissolved metal ions> 10 −6 mol / l. The passivity area with predominant formation of oxides and / or hydroxides, which can protect against further corrosion with high adhesive strength. However, a Pourbaix diagram cannot be used to read how strong the adhesive strength is. Furthermore, the rate of corrosion cannot be estimated. As a result, some scholars have questioned the practical use of these diagrams. In the immunity range, the value of dissolved metal ions is <10 −6 mol / l.
These diagrams were developed by Marcel Pourbaix in 1938 .
See also
literature
- M. Pourbaix: Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions . National Association of Corrosion Engineers, 1974, ISBN 0-915567-98-9 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ulrich Bette, Markus Büchler: Pocket book for cathodic corrosion protection , 9th edition, Vulkan Verlag GmbH, Essen 2017, ISBN 978-3-8027-2868-6 , p. 22.
- ^ Paul Wehr, Hans-Rainer Sinning (Ed.): Corrosion of the materials . Faculty of Mechanical Engineering TU Braunschweig, Braunschweig 2009, p. 28-29 .