Protein ligation
The protein ligation ( English protein ligation ) is a biochemical method of protein synthesis by linking two or more peptides .
Reaction pathways
Protein ligation allows two peptides to be linked to one another. Usually these are peptide fragments that have been produced by solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). Various methods of protein ligation have been described, e.g. B .:
- the native chemical ligation
- the prior thiol capture
- the Expressed Protein Ligation
- the acyl-initiated capture
- the SEA native peptide ligation
- the intein coupling
- the peptide ligation with selenocysteine .
- and the traceless Staudinger ligation
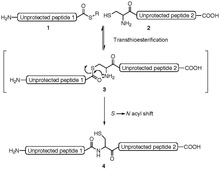
Native chemical ligation
The N -terminal peptide must for protein ligation as the last amino acid (at its C -terminus ) a thioester and the C -terminal peptide has for protein ligation as first amino acid (at its N -terminus a) cysteine have.
SEA native peptide ligation
The N -terminal peptide must for protein ligation as the last amino acid (at its C -terminus ) a bis (2-sulfanylethyl) amino group (SEA) and the C -terminal peptide has for protein ligation as first amino acid (at its N -terminus ) have a cysteine or homocysteine .
Staudinger ligation
The possibility of using the Staudinger reaction for peptide or protein ligation, discovered in 2000, is known as the Staudinger ligation. In contrast to “native peptide ligation”, the peptide linkage with the Staudinger ligation does not depend on a specific amino acid side chain. In the Staudinger ligation, a triarylphosphine oxide group remains in the vicinity of the amide bond; if this is not desired, the so-called traceless Staudinger ligation can be used, in which the phosphine oxide unit is split off in the hydrolysis step. This is achieved by using the phosphine diphenylphosphanyl-phenol or di-phenylphosphanylmethanethiol. Both phosphines show a good reaction profile and thus enable protein ligation in yields of up to 99%.
The use of the traceless Staudinger ligation enabled the synthesis of ribonuclease A from three peptide fragments.
history
The underlying reaction of native chemical ligation was published in 1953 by T. Wieland. From 1994 the reaction for the production of proteins from peptides was further developed by SB Kent. In 2000 Bertozzi et al. and Raines et al. the protein ligation with the Staudinger ligation.
literature
- T. Kimmerlin, D. Seebach: '100 years of peptide synthesis': ligation methods for peptide and protein synthesis with applications to beta-peptide assemblies. In: The journal of peptide research: official journal of the American Peptide Society. Volume 65, Number 2, February 2005, pp. 229-260, doi : 10.1111 / j.1399-3011.2005.00214.x , PMID 15705167 .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d e Maja Köhn, Rolf Breinbauer: The Staudinger Ligation - a gift for chemical biology . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 116 , no. 24 , June 14, 2004, pp. 3168-3178 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.200401744 .
- ↑ TW Muir, D. Sondhi, PA Cole: Expressed protein ligation: a general method for protein engineering. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 95, Number 12, June 1998, pp. 6705-6710. PMID 9618476 , PMC 22605 (free full text).
- ↑ BL Nilsson, MB Soellner, RT Raines: Chemical synthesis of proteins. In: Annual review of biophysics and biomolecular structure. Volume 34, 2005, pp. 91-118, doi: 10.1146 / annurev.biophys.34.040204.144700 . PMID 15869385 , PMC 2845543 (free full text).
- ↑ TW Muir, PE Dawson, SB Kent: Protein synthesis by chemical ligation of unprotected peptides in aqueous solution. In: Methods in enzymology. Volume 289, 1997, pp. 266-298. PMID 9353726 .
- ↑ TM Hackeng, JH Griffin, PE Dawson: Protein synthesis by native chemical ligation: expanded scope by using straightforward methodology. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 96, Number 18, August 1999, pp. 10068-10073. PMID 10468563 , PMC 17843 (free full text).
- ^ T. Wieland, E. Bokelmann, L. Bauer, HU Lang, H. Lau, W. Schafer: Polypeptide syntheses. VIII. Formation of sulfur containing peptides by the intramolecular migration of aminoacyl groups. In: Liebigs Ann Chem. Volume 583, 1953, pp. 129-149.
- ^ PE Dawson, TW Muir, I. Clark-Lewis, SB Kent: Synthesis of proteins by native chemical ligation. In: Science. Volume 266, Number 5186, November 1994, pp. 776-779. PMID 7973629 .
- ↑ S. Kent: Total chemical synthesis of enzymes. In: Journal of peptide science: an official publication of the European Peptide Society. Volume 9, Number 9, September 2003, pp. 574-593, doi: 10.1002 / psc.475 . PMID 14552420 .