Pseudo-obstruction
The pseudo-obstruction (also intestinal pseudo-obstruction) of the intestine is a technical term from medicine. It is used to describe a mostly massively distended, functionally motionless (= atonic) intestine without a mechanical cause . This condition also occurs with mechanical intestinal obstruction . The disease was first described in 1948 by the British surgeon Heneage Ogilvie (1887–1971), which is why the term Ogilvie syndrome is used synonymously. The clinical picture is rare, serious and occurs mainly in old people, after an operation or in the context of other, very serious diseases. If no such cause is found and the condition persists, it is called chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO).
Symptoms
The patients complain of stool retention, more or less severe pain in the abdomen and show a massively distended abdomen. In the event of complications , circulatory shock or respiratory failure can occur very quickly .
root cause
The etiology and pathogenesis of Ogilvie syndrome are unclear. A dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system with increased sympathetic activity is assumed to be the cause. Sometimes it occurs as a result of trauma, after surgery in the abdomen or pelvis , in various basic internal diseases such as chronic bronchitis or without an apparent cause. In chronic gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction, a paraneoplastic syndrome can also be present.
Diagnosis
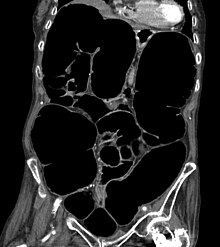
Diagnosing the disease is easy because the x-ray shows very characteristic signs. The entire large intestine is broadly filled with air, especially the ascending part of the large intestine often reaches a width of more than 10 cm.
- X-ray of the abdomen while standing
- Colon contrast enema
- Colonoscopy
- Computed tomography of the abdomen
Differential diagnosis includes constipation , mechanical ileus , toxic megacolon, and sigmoid volvulus.
Complications
The complication rate and mortality of the disease are high if air is not removed from the large intestine. The following complications can occur:
- Perforation (breakthrough in the intestinal wall)
- Intestinal ischemia ( circulatory disorder in the intestinal wall)
- Respiratory insufficiency due to the elevated diaphragm (impaired breathing )
therapy
- Medicinal measures:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors neostigmine or pyridostigmine
- Intravenous fluids
- Colon tube and enemas
- Gastric tube when vomiting
- Decompression using a colonoscopy
- Artificial anus at the caecum
Web links
- www.digestive-motility.org
- Pseudo-obstruction Knowledge Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Individual evidence
- ↑ Circulating antineural antibodies (Anti-Yo, Hu, Ri, Ma2, CV2, Amphiphysin). (PDF; 192 kB) Retrieved August 25, 2013 .
