Pulsed wave Doppler
When pulsed-wave Doppler , and pulsed Doppler or short PWD is a process for the exact location and speed measurement referred to by mass motions. The main application of the procedure is in heart and vascular diagnostics in medical ultrasound .
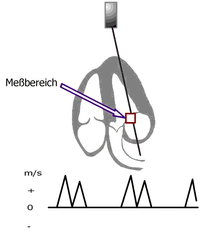
In addition to the continuous wave Doppler (CW Doppler), the PWD method is one of the conventional Doppler applications. With the pulsed Doppler, only a single piezo crystal of the ultrasonic probe is used for the measurement, as it is both the transmitter and receiver of the signal. After the crystal has sent a short ultrasonic signal, the device sets it to receive. A precisely defined point can now be calculated from the runtime of the signal. With the help of the Doppler effect , the movement in the area of the examined point (measuring area) in relation to the transducer is determined. The detected movement is plotted continuously along an abscissa (time axis), the abscissa representing the movement value zero. The measured speed is indicated on the ordinate in m / s or cm / s (see figure). Movements on the transducer are transferred above, movements away from the transducer below the zero line.
The main limitation of the method is the relatively low maximum detectable speed. Depending on the pulse repetition rate and penetration depth, aliasing occurs from a certain point . Although this phenomenon can be reduced by shifting the zero line, the determination of high velocities, such as occur with stenoses , shunts and insufficiencies , is not guaranteed and the spatially less precise CW Doppler must be used.