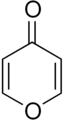
Pyron
Pyrones or pyranones are a group of cyclic chemical compounds from the group of oxygen-containing heterocycles . They contain an unsaturated six-membered ring with an oxygen atom and a keto group . There are two isomeric compounds: 2-pyrone and 4-pyrone . The 2-pyrone structure occurs naturally as part of the coumarin ring system and as part of several bacterial signaling molecules . 4-pyrone is also found in some natural chemical compounds such as maltol , kojic acid, and flavonoids .
The 4-pyrone structure is a component of meconic acid . The biosynthesis takes place from phenylalanine or tyrosine .
literature
- Introduction to Organic Chemistry , Andrew Streitwieser, Jr. and Clayton H. Heathcock, Third Edition, pp. 1038-1040. ISBN 0-02-418140-4 .
- Alexander O Brachmann, Sophie Brameyer u. a .: Pyrones as bacterial signaling molecules. In: Nature Chemical Biology. 2013, S., doi : 10.1038 / nchembio.1295 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ JK Weng, Y. Li, H. Mo, C. Chapple: Assembly of an evolutionarily new pathway for α-pyrone biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. In: Science. Volume 337, number 6097, August 2012, pp. 960-964, doi : 10.1126 / science.1221614 , PMID 22923580 .