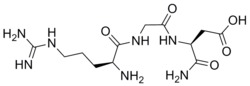
RGD sequence
The RGD sequence is an amino acid sequence made up of the three L - amino acids arginine , glycine and aspartic acid , Arg-Gly-Asp for short, or in the one -letter code RGD.
The RGD sequence occurs particularly in proteins of the extracellular matrix (connective tissue), for example in fibronectin and vitronectin . Cells can bind to the RGD sequence with the help of certain cell surface receptors, the integrins .
RGD-mediated cell adhesion is used for mechanical anchoring of cells. In addition, various cell responses are generated, e.g. B. Formation of focal adhesion complexes, polarization of the cell, survival signals. The human cytomegalovirus has an RGD sequence for cell adhesion.
Implants can be coated with the RGD sequence for better integration into the body. Non-immobilized RGD peptides and non-peptide analogs are intended to prevent tumor-induced new formation of blood vessels (neoangiogenesis) or undesired blood clotting.
The RGD sequence is presented in the various matrix proteins in different conformations, some of which are specifically recognized by the integrin subtypes. The development of integrin subtype-specific cyclic RGD peptides, such as cilengitide, is based on this principle . In addition to the RGD sequence, other peptide sequences for integrin-mediated cell adhesion are known.
Individual evidence
- ↑ J. Murata, I. Saiki: [Inhibition of tumor metastasis by synthetic peptide analogues of cell-adhesive RGD sequence of fibronectin]. In: Nihon rinsho. Japanese journal of clinical medicine. Volume 53, Number 7, July 1995, pp. 1653-1659, ISSN 0047-1852 . PMID 7630003 .
- ↑ LC Loh, D. Locke, R. Melnychuk,. La: The RGD sequence in the cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase accessory protein can mediate cell adhesion. In: Virology. Volume 272, Number 2, July 2000, pp. 302-314, ISSN 0042-6822 . doi : 10.1006 / viro.2000.0366 . PMID 10873773 .
- ↑ F. Danhier, A. Le Breton, V. Préat: RGD-based strategies to target alpha (v) beta (3) integrin in cancer therapy and diagnosis. In: Molecular pharmaceutics. Volume 9, Number 11, November 2012, pp. 2961-2973, ISSN 1543-8392 . doi : 10.1021 / mp3002733 . PMID 22967287 .
- ^ M. Barczyk, S. Carracedo, D. Gullberg: Integrins. In: Cell and tissue research. Volume 339, Number 1, January 2010, pp. 269-280, ISSN 1432-0878 . doi : 10.1007 / s00441-009-0834-6 . PMID 19693543 . PMC 2784866 (free full text).