Radical cation
| Formation of a radical cation by single electron transfer (SET) |
| Formation of a radical cation by elimination (removal) of an electron from a neutral molecule A . |
| Wurster salts (selected mesomeric boundary structures ) |
|---|
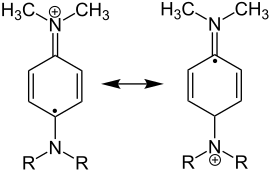 Wurster salts - general formula - (R = alkyl, H) |
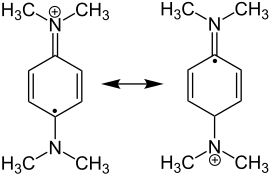 Wurster reagent |
Radical cation is the collective name for a group of molecules that have both the characteristic of a radical (a "lone" electron) and the positive electrical charge of a cation .
Wurster salts are among the radical cations.
Manufacturing
Radical cations formed during the single-electron transfer ( single electron transfer , SET) on or from neutral molecules. This ionization of molecules is z. B. observed in the mass spectrometer when molecules are bombarded with electrons. The polarographic oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons also leads to the formation of radical cations.
Spectroscopic properties
Radical cations and radical anions of aromatic hydrocarbons have very similar electronic spectra .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 5: Pl-S. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1987, ISBN 3-440-04515-3 , p. 3462.
- ↑ a b c Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (coordinators): Lexicon of Chemistry in three volumes, Spektrum Verlag, Heidelberg, Volume 3, 1999, ISBN 3-8274-0381-2 , p. 139.