Red Clump Star
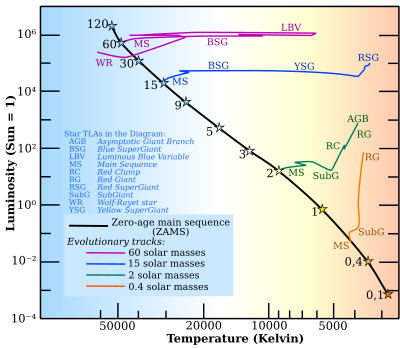
Red Clump Stars ( German translation Red lump-star ) are developed metal-rich stars with a helium-burning core in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and meet the stars of the horizontal branch of the Population II . Due to the low dependence of their luminosity on metallicity, they are used to determine astronomical distances.
development
After the end of the central hydrogen burn on the main sequence , stars of medium mass with 0.5 to 2.5 solar masses initially develop a bowl-shaped hydrogen burn, while the ashes of the thermonuclear reactions accumulate in the core of the star. The star develops along the giant red branch to higher luminosity and lower effective temperatures . The pressure and the temperature in the core increase until a stable helium flame ignites. Depending on the metallicity of the stars, stars with a low level of metal migrate to higher temperatures due to their low opacity and form a horizontal load in the color-brightness diagram . Metal-rich stars in population I, on the other hand, remain red giants and form a heavily occupied red clump in the HR diagram, as the stars remain in this position during the phase of central helium burning.
Distance determination
In the infrared , the absolute brightnesses of the Red Clump Stars are only subject to a slight scatter. The absolute brightness M K is −1.54 to −1.57 over an age range of 0.31 to 8 billion years for solar abundances. This low scatter in combination with a low absorbance in the mid-infrared makes the Red Clump Stars a preferred means of determining distances. They are used to analyze structures within the Milky Way and the local group .
Examples
Individual evidence
- ↑ S. Bilir et al .: Luminosity-Color Relations for Red Clump Stars . In: Astrophysics. Solar and Stellar Astrophysics . 2012, arxiv : 1210.5352v1 .
- ↑ S. Karaali et al .: Absolute Magnitude Calibration for Red Clump Stars . In: Astrophysics. Solar and Stellar Astrophysics . 2013, arxiv : 1304.2530v1 .
- ↑ G. Tautvaisiene et al .: Red clump stars of the Milky Way - laboratories of extra mixing . In: Astrophysics. Solar and Stellar Astrophysics . 2013, arxiv : 1304.4393v1 .
- ^ Smitha Subramanian, Annapurni Subramaniam: Structure of the Large Magellanic Cloud from Near Infrared Magnitudes of Red Clump Stars . In: Astrophysics. Solar and Stellar Astrophysics . 2013, arxiv : 1301.7538v1 .
- ↑ S. Bilir et al .: A New Absolute Magnitude Calibration for Red Clump Stars . In: Astrophysics. Solar and Stellar Astrophysics . 2013, arxiv : 1303.3292v1 .