South Indian spiny billy
| South Indian spiny billy | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

South Indian Stachelbilch ( Platacanthomys lasiurus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Platacanthomys | ||||||||||||
| Blyth , 1859 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Platacanthomys lasiurus | ||||||||||||
| Blyth , 1859 |
The South Indian Stachelbilch ( Platacanthomys lasiurus ) is a rodent in the family Stachelbilche (Platacanthomyidae) and is the only species of its genus today . The extinct species Platacanthomys dianensis was described in the genus .
features
The species reaches a head-trunk length of 13 to 20 cm and a tail length of 7.5 to 10 cm. The weight is around 75 grams. The fur on the thin undercoat is interspersed with many spines. Finer spines are also found on the underside. The tail has a bushy tassel at the end and is usually darker than the fur on the top. The back and upper sides of the body are brownish, the lower areas are whitish. Reddish tones can also predominate on the top of the head.
Distribution and habitat
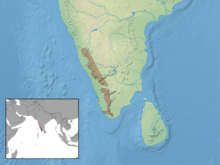
The South Indian Stachelbilch occurs in the southern Western Ghats in India . There he lives at altitudes between 600 and 2,000 meters above sea level. NN . He stays in forests of different moisture.
Way of life
These animals build their burrows in crevices and tree hollows by padding the opening with leaves and moss. The South Indian Stachelbilch feeds mainly on fruits, grains and other seeds, as well as roots. Caged specimens were less active and aggressive towards humans during the day. Reproduction generally takes place in the rainy season. In one female, four young animals were registered in the litter. A specimen lived 20 months after it was caught.
status
This spiny billy is very sensitive to changes in habitat. It is caught in certain areas and different parts of the body are used in traditional medicine. The IUCN lists the species as endangered ( vulnerable ).
Individual evidence
- ^ Wilson & Reeder (eds.): Mammal Species of the World . 3. Edition. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 2005, ISBN 0-8018-8221-4 (English, Platacanthomys ).
- ↑ a b c Nowak, RM (1999) pp. 1431/32
- ↑ a b B. Lundrigan (2003). Platacanthomys Lasiurus (Engl.) Animal Diversity Web . University of Michigan. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- ↑ a b Platacanthomys Lasiurus in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2011. Posted by: Molur, S. & Nameer, PO, 2008. Accessed September 4 2012th
- ^ Gray, Charles: Note on the Malabar spiny mouse ( Platacantomys lasiurus ) . In: Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society . 18, 1908, p. 679.
literature
- Ronald M. Nowak: Walker's Mammals of the World . Johns Hopkins University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-8018-5789-9