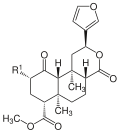
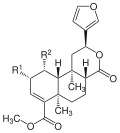
Salvinorine
The salvinorins are a group of structurally closely related diterpenoid secondary metabolites of the Aztec sage ( Salvia divinorum ).
Overview
Salvinorin A was isolated in 1982 as the first substance out of nine individual representatives of salvinorins (A – H, J) . Salvinorin A is a hallucinogen with dissociative effects. Salvinorine B – E are considered to be psychotropically inactive, Salvinorin F has no known psychotropic effects. Salvinorin A was identified as a selective agonist of κ opioid - receptor . Binding to this receptor has also been demonstrated for salvinorin G in low concentrations.
Salvinorin A is the most potent known naturally occurring psychoactive substance, with an effective dose from 200 µg . It is noticeable that in contrast to other natural hallucinogens such as DMT , psilocybin or mescaline , or comparable synthetic drugs such as LSD or 2C-B , the substance does not have a basic nitrogen atom.
| Surname | structure | R 1 | R 2 | Molecular formula | molar mass | CAS number | PubChem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salvinorin A | -OCOCH 3 | - | C 23 H 28 O 8 | 432.46 g mol −1 | 83729-01-5 | 128563 | |
| Salvinorin B | -OH | - | C 21 H 26 O 7 | 390.43 g mol −1 | 92545-30-7 | 11440685 | |
| Salvinorin C | -OCOCH 3 | -OCOCH 3 | C 25 H 30 O 9 | 475.29 g mol −1 | 385785-99-9 | - | |
| Salvinorin D | -OCOCH 3 | -OH | C 23 H 28 O 8 | 432.47 g mol −1 | 540770-13-6 | - | |
| Salvinorin E | -OH | -OCOCH 3 | C 23 H 28 O 8 | 432.47 g mol −1 | 540770-14-7 | - | |
| Salvinorin F | -OH | -H | C 21 H 26 O 6 | 374.43 g mol −1 | 540770-15-8 | - | |
| Salvinorin G | = O | -OCOCH 3 | C 23 H 26 O 8 | 430.45 g mol −1 | 866622-54-0 | - | |
| Salvinorin H | -OH | -OH | C 21 H 26 O 7 | 390.43 g mol −1 | 872004-62-1 | - | |
| Salvinorin I | - | - | C 21 H 28 O 7 | 392.45 g mol −1 | 917951-71-4 | - | |
| 17 α- salvinorin J. | 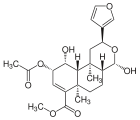 |
- | - | C 23 H 30 O 8 | 434.49 g mol −1 | 1157894-83-1 | - |
| 17 β- salvinorin J. | 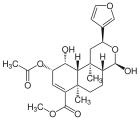 |
- | - | C 23 H 30 O 8 | 434.49 g mol −1 | 1157894-85-3 | - |
The isolation of another compound that can be assigned to the salvinorines was recently published. The structure of salvinorin J is similar to that of salvinorin E, however, C-17 is not formed as a lactone , but as a hemiacetal .
Synthetically produced salvinorin analogs
Due to their high pharmacological effectiveness, further derivatives have now been produced synthetically, some of which are even more effective than salvinorin A on the κ-opioid receptor. Structurally related substances are also Herkinorin , Divinatorin and Salvinicin .
Legal status
In Germany, with the 21st BtMÄndV, Salvia divinorum (plants and plant parts) was included in Appendix I of the BtMG and is therefore one of the “non-marketable narcotics”.
literature
- DM Turner: Salvinorin: The Psychedelic Essence of Salvia Divinorum . Panther Press, 1996, ISBN 0-9642636-2-9 (English).
- Jochen Gartz: Salvia divinorum - The fortune telling sage . Nachtschatten Verlag, 2001, ISBN 3-907080-28-9 , 80 pages.
- Bastian Borschke: Salvia Divinorum and other psychoactive species of sage . Grüne Kraft, 2002, ISBN 3-930442-55-8 , 32 pages.
- Salvia divinorum . In: Entheogene Blätter , Issue # 16, 09/2003, ISSN 1610-0107 .
- Thomas E. Prisinzano, Richard B. Rothman: Salvinorin A Analogs as Probes in Opioid Pharmacology . In: Chemical Reviews , 2008, 108, pp. 1732-1743. doi: 10.1021 / cr0782269
Web links
- Daniel Siebert: Salvinorin (English)
Individual evidence
- ^ A Ortega, JF Blount, PS Manchand: Salvinorin, a new trans-neoclerodane diterpene from Salvia divinorum (Labiatae) . In: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 . 1982, pp. 2505-2508. doi : 10.1039 / P19820002505 .
- ↑ KA MacLean, MW Johnson, CJ Reissig, TE Prisinzano, RR Griffiths: Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. In: Psychopharmacology. Volume 226, number 2, March 2013, pp. 381-392, doi : 10.1007 / s00213-012-2912-9 , PMID 23135605 , PMC 3581702 (free full text).
- ↑ BL Roth et al .: Salvinorin A: A potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous opioid selective agonist . In: PNAS . Volume 99, 2002, pp. 11934-11939. PMID 12192085 doi: 10.1073 / pnas.182234399 .
- ↑ Timothy A. Vortherms, Bryan L. Roth: Salvinorin A - From Natural Product to Human Therapeutics. In: Molecular Interventions , 2006, Vol. 6, No. 5, pp. 257-265. doi: 10.1124 / mi.6.5.7 .
- ^ DJ Siebert: Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings. (PDF; 284 kB) In: J. Ethnopharmacol , Volume 43, 1994, pp. 53-56. PMID 16426651 .
- ↑ R. Marushia: Salvia divinorum: The Botany, Ethnobotany, Biochemistry and Future of a Mexican Mint. ( Memento of the original from October 7, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 54 kB) In: Ethnobotany , 2002
- ↑ Lukasz Kutrzeba, Ferreira, Zjawiony: Salvinorins J from Salvia divinorum: Mutarotation in the Neoclerodane System . In: J. Nat. Prod . 72, No. 7, 2009, pp. 1361-1363. doi : 10.1021 / np900181q .
- ↑ TA Munro, KK Duncan, W Xu, Y Wang, LY Liu-Chen, WA Carlezon, BM Cohen, C Béguin: Standard protecting groups create potent and selective kappa opioids: salvinorin B alkoxymethyl ethers . In: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry . 16, No. 3, February 2008, pp. 1279-86. doi : 10.1016 / j.bmc.2007.10.067 . PMID 17981041 . PMC 2568987 (free full text).