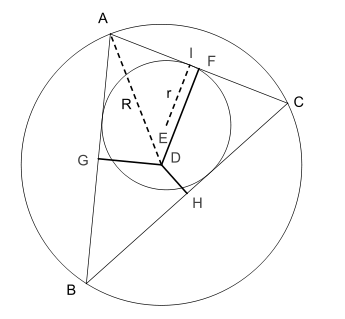
Carnot's theorem (circumference, incircle)
The set of Carnot (after Lazare Nicolas Marguerite Carnot in any) describes triangle a relationship between Inkreisradius , within radius and the distances of the radius center point of the triangle sides. It says that the sum of the signed distances is equal to the sum of the inscribed radius and the circumferential radius.
Here the radius of the circumference with the center and the radius of the inscribed circle with the center of a triangle . The points are the base points of the perpendicular to the sides of the triangle. The function returns the length of a line if it is wholly or partially inside the triangle and the negative length if it is completely outside the triangle.
In the special case of the acute-angled and right-angled triangles, the signed distances are not all negative, so that in this case the sum of all distances can simply be used.
| obtuse triangle | acute triangle |
|---|---|
literature
- The root. Issue 7/2000, p. 170.
- Claudi Alsina, Roger B. Nelsen: When Less is More: Visualizing Basic Inequalities . MAA, 2009, ISBN 978-0-88385-342-9 , p. 99. (books.google.de)
- Frédéric Perrier: Carnot's Theorem in Trigonometric Disguise. In: The Mathematical Gazette. Volume 91, No. 520, March, 2007, pp. 115-117 ( JSTOR 40378302 )
- David Richeson: The Japanese Theorem for Nonconvex Polygons - Carnot's Theorem. In: Convergence. December 2013.
Web links
- Eric W. Weisstein : Carnot's theorem . In: MathWorld (English).
- Florian Modler: Forgotten sentences on the triangle - Carnot's sentence on Matroids Matheplanet
- Carnot's theorem. on cut-the-knot.org