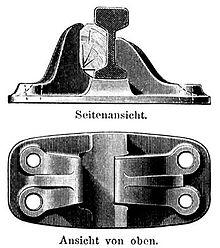
Rail chair
As a rail chair , the device is referred to, a railroad rail for mounting on a crosstie receives. The term ( chairs ) comes from English and was adopted with the first railways delivered from England.
The first rail chairs were cast iron profiles that were attached to stone cubes with dowels and nails (e.g. on the Bavarian Ludwig Railway ). In their recess, they took the much smaller double head rails or special “chair rails” used at the time and also supported them laterally. A wooden wedge was driven between the higher external chair “backrest” and the rail web to fix it. The inner web side of the rail lay directly on the lower, curved inner “backrest” of the chair. In the 20th century, the wooden wedges were increasingly replaced by steel tension clamps.
With the advent of the wide base or Vignole rail , new fasteners had to be introduced. This will no longer be called a rail chair but according to their design as inguinal, hooks or ribbed plates, the latter example, the rail fastening system . The designs are very different, they are not only matched to the type of fastening (screws, clamps, etc.) and the threshold material (wood, steel or concrete), but also, depending on the requirements, to particularly precise tracking , subsequent correction options or particularly good noise insulation.
While the support plates are normally screwed onto wooden and concrete sleepers with sleeper screws, they are usually welded onto steel sleepers or pushed into a groove and braced. In the case of tracks with low requirements, which are also frequently re-laid (e.g. field and lightly built narrow-gauge railways ), the use of underlay panels was often completely dispensed with.
Like other base plates, rail chairs are part of the small iron.
In the Anglo-American language area, the term “rail chair ” is also used for the assembly equipment for the conductor rails ( third rail ). Due to the special requirements of electrical insulation and the position of the area covered by the pantographs, these each have very special shapes. In the German-speaking world, the term power rail holder is used for this .
Examples of various rail fastenings
Older rail chair at the SNCF
Superstructure K , sleeper screws hold the ribbed plate on the concrete sleeper and two hook screws with clamping plates hold the rail