Schottky TTL
Schottky TTL (S-TTL) is a family of logic that designates a specific semiconductor technology for integrated circuits (ICs). You use a Schottky diode as negative feedback for the transistors of the 2nd stage (the 2nd T or the push-pull stage) (see OpAmp). These transistors are used in a common emitter configuration. The voltage and the current are normally amplified in an inverted manner. While the transistors ensure a steep edge between the TTL voltage levels, the small diodes with a low capacitance prevent the voltage from being overshooted far beyond the hi or low voltage. Due to the high current gain, the feedback hardly loads the amplifier, although the power requirement naturally increases somewhat.
It uses so-called "Schottky transistors" to reduce switching times and throughput times through logic gates compared to conventional transistor-transistor logic (TTL) based on bipolar transistors .
description
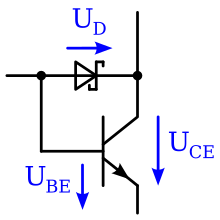
Schottky TTL technology is based on the use of a Schottky diode , which bridges the base and collector of a bipolar transistor , which is then referred to as a "Schottky transistor". With a positive base-emitter voltage and a conductive transistor, the diode is in the forward direction and prevents the collector-emitter voltage from falling below approx. 0.3-0.4 volts. The transistor does not reach full saturation, which results in a faster switching time than with TTL. To distinguish these transistors in the circuit diagram and to avoid having to constantly draw in this additional Schottky diode, a separate circuit symbol is used for those transistors whose base-collector section is bridged with a Schottky diode.
S-TTL components were the first TTL components that could compete with the speed of ECL technology.
application
The Schottky series are identified by adding the letter "S". There are the following families of Schottky series:
- Schottky-TTL (S-TTL), designation 74S
- Low-Power-Schottky-TTL (LS-TTL), designation 74LS
- Advanced-Low-Power-Schottky-TTL (ALS-TTL), designation 74ALS
- Advanced Schottky TTL (AS-TTL), designation 74AS
- Fairchild Advanced Schottky TTL (F-TTL), designation 74F
LS-TTL series ICs were inexpensive and widespread, but are rarely used anymore. They had a speed-performance product improved five times and an 80 percent reduction in power requirements over standard TTL. The further development ALS-TTL is about 30% faster than LS-TTL. AS-TTL is the fastest TTL series. The F-TTL series named after the manufacturer Fairchild is optimized for the lowest possible power consumption. Series in standard TTL technology usually have the family designation 74.
ICs with the same semiconductor technology can be interconnected without any problems. This is why one speaks of series when ICs with different functions are manufactured using the same technology.
history
In 1956, Richard H. Baker described a circuit, known as a Baker clamp circuit , to keep the bipolar transistor in a switching application out of saturation with the aid of two additional diodes. Baker pursued the goal of reducing the switching times of bipolar transistors by avoiding the saturation caused by the two diodes and negative feedback . The Baker clamping circuit uses two different types of diodes , a germanium diode (Ge) in the feedback branch and a silicon diode (Si) with different forward voltages . Schottky diodes were not yet available at the time.
In 1964, James Robert Biard published a patent on the "Schottky transistor" circuit, then employed by Texas Instruments , which is based on the Baker clamp circuit. In contrast to the Baker circuit, Schottky transistors can easily be implemented in integrated circuits (ICs), which opened up the possibility of developing the S-TTL logic gates.
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Richard H. Baker: Maximum Efficiency Switching Circuits . MIT Lincoln Laboratory Report TR-110, 1956 ( online ).
- ↑ Patent US3463975 : Unitary Semiconductor High Speed Switching Device Utilizing a Barrier Diode. Published December 31, 1964 , inventor: James R. Biard.