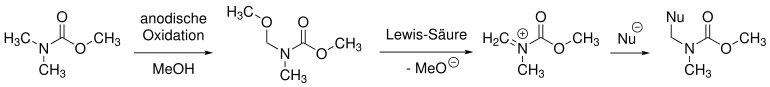Shono oxidation
The Shono oxidation is an electro-organic reaction in which CC bonds in the α-position are linked to an amino group by anodic oxidation . The reaction was named after Tatsuya Shono (* 1929), who first described this reaction in 1981.
Overview reaction
Shono first described the anodic oxidation of carbamates. Here, methanol is used both as a coupling partner and as a solvent. The functionalization takes place in the α-position to the amine group. Under the action of a Lewis acid (often TiCl 4 ), a methanolate anion (MeO - ) can be eliminated and an iminium cation is formed . A new bond is formed through reaction with a (carbon) nucleophile (Nu - ).
mechanism
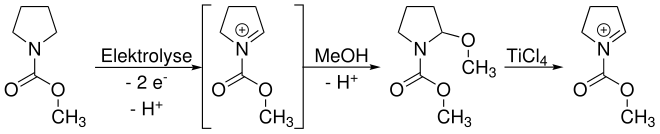
In principle, two reaction paths are possible. The route shown in the overview reaction shows the trapping of an intermediate iminium ion by methanol. Since this iminium is needed again for the subsequent functionalization, it has to be released again by a Lewis acid - here titanium (IV) chloride . The trapping is necessary here, as most nucleophiles used for the functionalization are not stable under the usual electrolytic conditions.
The trapping can be circumvented by electrolysis at low temperatures. In non-nucleophilic solvents, the iminium is sufficiently stable to be reacted directly with a nucleophile after the electrolysis is complete.
The production and subsequent conversion of iminium ions, but also other organic cations, is known as the cation pool method .
application
The oxidation can Shono in the synthesis of some bioactive substances such as, for example, (+) - myrtin, iminosugars , ropivacaine or chiral cyclic amino acids , can be used.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Tatsuya Shono, Yoshihiro Matsumura, Kenji Tsubata: Electroorganic chemistry. 46. A new carbon-carbon bond forming reaction at the α-position of amines utilizing anodic oxidation as a key step . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 103 , no. 5 , March 1981, pp. 1172–1176 , doi : 10.1021 / ja00395a029 .
- ↑ Seiji Suga, Masayuki Okajima, Jun-ichi Yoshida: Reaction of an electrogenerated 'iminium cation pool' with organometallic reagents. Direct oxidative α-alkylation and -arylation of amine derivatives . In: Tetrahedron Letters . tape 42 , no. 11 , March 2001, p. 2173-2176 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (01) 00128-9 .
- ↑ Jun-ichi Yoshida, Seiji Suga: Basic Concepts of “Cation Pool” and “Cation Flow” Methods and Their Applications in Conventional and Combinatorial Organic Synthesis . In: Chemistry — A European Journal . tape 8 , May 2002, pp. 2650-2658 , doi : 10.1002 / 1521-3765 (20020617) 8:12 <2650 :: AID-CHEM2650> 3.0.CO; 2-S .
- ^ Alan M Jones, Craig E Banks: The Shono-type electroorganic oxidation of unfunctionalized amides. Carbon – carbon bond formation via electrogenerated N-acyliminium ions . In: Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry . tape 10 , December 18, 2014, ISSN 1860-5397 , p. 3056-3072 , doi : 10.3762 / bjoc.10.323 .