Tachocline region
The Tachocline region or Tachocline for short is a term from solar physics . It describes the transition area between two zones of the sun that differ in their rotation :
- the interior of the sun rotates like a rigid body with a period of rotation of a little less than 27 days
- the outer areas rotate with 25.4 days at the equator and 36 days at the poles .
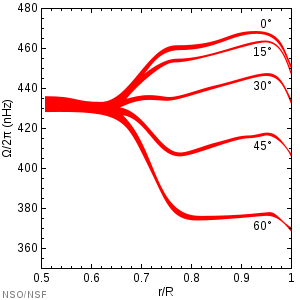
The Tachocline is therefore characterized by a high differential rotation . It has a thickness of about r t = 0.04 solar radii (data vary due to different definitions).
The tachocline is near the equator to r t = 0.693 ± 0.003 R ☉ and at 60 ° to r t = 0.717 ± 0.003 R ☉ centered ( prolate shape). Thus, the tachocline is in the vicinity of the interface between the radiant zone and the convection zone , the at r t = 0.713 ± 0.003 R ☉ is, but so far in no variation with solar width was determined.
literature
- Mark S. Miesch: Large-Scale Dynamics of the Convection Zone and Tachocline , Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2, (2005), 1. URL (cited on <April 22, 2005>): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2005-1
swell
- ↑ a b Mark S. Miesch: Large-Scale Dynamics of the convection zone and tachocline , Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2, (2005), 1. URL (cited on <June 9, 2006>): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2005-1