Termination step
The term termination step is used in both biology and chemistry in the formation of macromolecules. The further chain extension of a macromolecule is prevented by the termination step.
biology
In biology, translation is the term used to describe the synthesis of proteins in the cells of living organisms, which takes place on the ribosomes according to genetic information (see also protein biosynthesis ). In prokaryotes , the end of translation (termination) is reached when one of the stop codons UAG, UAA or UGA appears in the A-site of the ribosome. Since there is no suitable tRNA for these codons in the cell, translation then stops.
The termination of the synthesis of an mRNA is called transcription termination.
chemistry
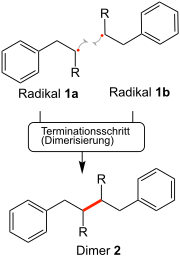
The termination of a radical chain reaction (e.g. chain polymerization ) through the dimerization of two radicals 1a and 1b with the formation of a non- radical compound 2 is called a termination step:
Low molecular weight molecules
The termination step through the recombination of two radicals is not limited to the formation of macromolecules. In other radical reactions too - such as the photobromination of ethane and other alkanes - the dimerization of two radicals is called a termination step.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Paula Yurkanis Bruice: Organic Chemistry , Pearson Education Inc., 2004, 4th edition, pp. 1427-1432, ISBN 0-13-121730-5 .
- ↑ Paula Yurkanis Bruice: Organic Chemistry , Pearson Education Inc., 2004, 4th edition, pp. 556-558, ISBN 0-13-121730-5 .