Thioacids
| Thioacids |
|---|
 Thionic acid |
 Thiol acid |
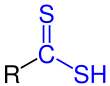 Dithioic acid |
| R is an organyl group . The functional groups are marked in blue . |
Thio acids (from the old Gr. Thio for sulfur) are a class of compounds that can be understood as sulfur derivatives of oxygen acids in which one or more oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms. These include both inorganic and organic acids (especially thiocarboxylic acids).
For example, thiosulfuric acid (H 2 S 2 O 3 ) is a thio acid of sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ). Known derivatives of thioacids are e.g. B. Esters of thiophosphoric acids , which are used as insecticides . From the dithiocarbonic the so-called lead xanthate from. Cellulose xanthogenate is an important intermediate product in the viscose process for the production of cellulose fibers .
Monothiocarboxylic acids
Monothiocarboxylic acids can be described as tautomeric thionic acid R – CS – OH or thiolic acid R – CO – SH. As a rule, they are only stable in the form of their salts or covalent derivatives (for example thiolesters ). Volatile thiocarboxylic acids have a very unpleasant odor.
Dithiocarboxylic acids
Dithiocarboxylic acids have the general structure R – CS – SH. As a rule, they are also only stable in the form of their salts or covalent derivatives.
synthesis
The reaction of Grignard compounds with carbon disulfide (CS 2 ) gives salts of the relevant dithiocarboxylic acid . The dithiocarboxylic acid is obtained by acidification.
literature
- Entry to thioacids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 8, 2014.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Albert Gossauer: Structure and Reactivity of Biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, pp. 413-414, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ Michael B. Smith: March's advanced organic chemistry , John Wiley & Sons, 7th edition, 2013, p. 1132, ISBN 978-0-470-46259-1 .