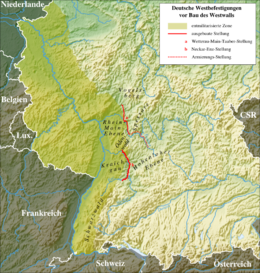
Wetterau-Main-Tauber position
The Wetterau-Main-Tauber-position ( WMTS ) was a military bunker belt built between 1936 and 1937 between Büdingen in the Wetterau and the Lower Franconian Klingenberg in Bavaria .
Together with the Neckar-Enz position and the Bavarian-Czech border position , it was supposed to protect the German Empire from a rapid attack from East and West, which could have led to the separation of the southern half of Germany. In keeping with the regulations of the Versailles Treaty, its location ultimately chosen offered the most westerly, tactically and technically sensible possibility of delaying the advance of an attacker.
The plans were originally much more extensive: In addition to positions for gun batteries up to a caliber of 28 cm, mortar casemates were also planned. The position north of Büdingen was to be expanded to a particularly low level. Ultimately, a total of 328 bunkers were built, as they were also implemented on the (later so-called) Siegfried Line at the same time . No concrete anti-tank barriers have been erected yet . Instead, tank trenches were dug in some places or wooden stakes were driven into the ground.
During the Second World War , the Wetterau-Main-Tauber position no longer played a role, as their bunkers were de facto ineffective until 1945 due to the further development of weapon technology and the Wehrmacht therefore no longer seriously considered using the position for defense.
Most of the bunkers were blown up after the war, and many were filled with earth in the decades that followed.
The Kleinwallstädter Schleuse is still worth seeing today. It was reinforced as a weir and reinforced with a bunker that is still preserved today.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Till Kiener: The Neckar-Enz position. Introduction to history and technology. Self-published, Nürtingen 2000 (booklet for the visit to the Ro 1 Bissingen museum bunker).
- ^ A b c Matthias Schneider: Little Siegfried-line. The history of the Wetterau-Main-Tauber position. S. Roderer Verlag, Regensburg 1997, ISBN 3-89073-169-4 ( theory and research, history 7).