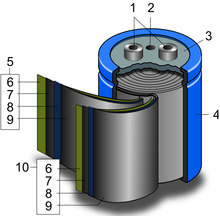
Winding capacitor
Winding capacitor is an ancient generic term for all electrical capacitors with a winding as a capacitor cell.
history
The term wound capacitor comes from the early days of the development of communications technology in the 1920s. The first electrical capacitors of modern times were aluminum electrolytic capacitors , the folded anode of which was located in large cups filled with liquid electrolyte, or layered mica capacitors , the so-called block capacitors . It was not until the invention of paper capacitors at the end of the 1920s that the principle of layering electrodes was abandoned because longer strips of paper covered with thin metal foils, in contrast to mica, could also be wound. The wound capacitor , at that time a paper capacitor, achieved the required reduction in dimensions with which the radio devices could reach a practical size.
A little later, in the mid-1930s, a further downsizing of the devices became possible through the invention of a new type of aluminum electrolytic capacitors with wound anode and cathode foils, which contained a paper layer as a carrier for the electrolyte. Despite completely different electrical properties (electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors), the new wound "aluminum electrolytic capacitors" were also carried under the now misunderstood term wound capacitor .
In the following period, with the development of the metallized paper capacitors (MP capacitors), the tantalum electrolytic capacitors and the plastic film capacitors, other capacitor families came onto the market, which also contain all designs that have a coil as a capacitor cell. As a result, the problem nowadays arises that the term wound capacitor no longer allows a meaningful definition, because these capacitor families not only have capacitive cells manufactured using winding technology, but all capacitive cells manufactured using other technologies.
- Plastic film capacitors are also available in a layered structure (stacked versions)
- Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are also available with a meandering folded version (SAL electrolytic capacitors)
- Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are mainly manufactured in sintered SMD design
Classification and designation
There are the following types of wound capacitors:
- Paper capacitors , not polarized
- MP capacitors , without polarity
- Plastic film capacitors (Folko), without polarity
- Aluminum electrolytic capacitors (Elko), polarized
- Tantalum electrolytic capacitors (Tako), polarized
- Double layer capacitors
Because of the completely different production processes and the different functionality (polarized / non-polarized) of the "Folkos" compared to the "Elkos" or "Takos" and which is nowadays according to the applicable standards (IEC 60384-1) with a completely different division into corresponding "capacitor families" the term wound capacitor is nowadays only justifiable as "laboratory jargon ".
In laboratory and hobbyist circles, the term wound capacitors is generally understood to mean “film capacitors”, or more precisely “plastic film capacitors”. In the field of training and teaching in the German-speaking area, all of the above-mentioned electrical capacitors that have a coil as a cell are often called wound capacitors , although the industry has not used this term as a generic term for various capacitor families for more than 40 years (IEC 384, Nov . 1968).