Xgrid
Xgrid is a concept of grid computing and distributed computing that was developed by Apple Inc. for the Mac OS X operating system . The solution is characterized by simple configurability and fully implemented support by the operating system . There are now solutions that can be used to integrate other systems into Xgrid (e.g. Windows or Linux )
Basics
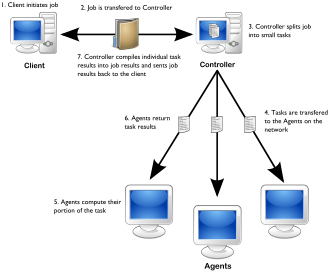
As usual in grid computing, Xgrid uses three components:
- Xgrid agent
- Xgrid controller
- Xgrid client
The agent runs on every node in the cluster, i.e. every computer that makes its resources available, and accepts the jobs. The controller controls the grid as a central administrative unit. After all, the client is the program that requests the grid resources. Agents can be set up on numerous operating systems and integrated into the Apple Xgrid. There are also updates for older Mac OS X systems, solutions for Unix and Linux and Java solutions that are independent of the operating system and therefore also run on Microsoft Windows operating systems.
hardware
In practical terms, all that hardware is needed is a computer with a network connection. On these grid computers, software takes on the task of solving a partial task, which a - usually central - server makes available. This server uses software that can split a large task into a number of subtasks for all nodes in the grid and summarize the partial results again.
software
The first implementation of this idea took place in OPENSTEP with the demo application "zilla.app". In Mac OS 10.4 (Tiger) and 10.5 (Leopard), all necessary components are already fully integrated in the system and only need to be activated (agents and controllers). Updates for Xgrid are available for older Mac OS X versions (Panther). Alternative operating systems have been supported by third-party software for some time.
See also
Web links
- Apple Xgrid for all systems - German instructions for installation