Time-cost-progress diagram
A time-cost-progress diagram in the project planning visualizes the current status of costs , the planned dates and the project progress , in order to make any deviations in the course of the project clear.
Action
During the project planning, labor values (A1, A2 ...) are defined, which should occur at a certain point in time at fixed costs. The actual labor values are then compared with the expected ones in order to determine differences such as cost overruns or delays .
This diagram is one of many project management techniques and tools . It is used in the process-cost-value analysis (car) as a starting point for value analysis of business processes . In practice, a corresponding project management software is used, whereby the generation of data is very important.
Advantages and disadvantages
| advantages | disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
Illustration
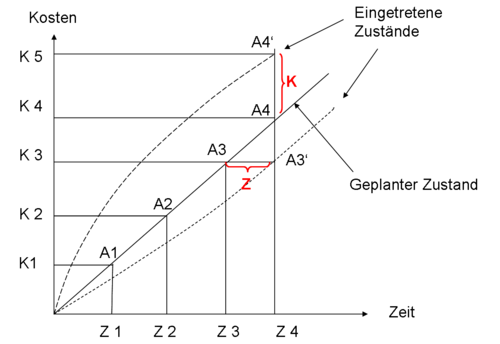
The following illustration shows a time-cost-progress diagram , where K stands for cost overrun, Z for time delay and A for labor value. A3 'means that the work value A3 was not reached at the planned time Z3, but only at the time Z4. However, the costs K3 were not exceeded. A4 'means that the labor value A4 was indeed reached at the planned date Z4, but with an excess of the costs of Δ K, that is to say at the costs K5.
Alternatives
- Bar chart (Gantt chart)
The Gantt chart shows the time sequence of projects and their sub-steps. In particular, a direct reference to the calendar is established. In the simplest case, it is a simple bar chart and was developed by Henry L. Gantt while working as a technical consultant for management.
The network plan technique is a useful tool to better plan and coordinate complex work processes as well as their logical links and temporal conditions. The best known methods are the method of the critical path ( critical path method ), PERT ( Program Evaluation and Review Technique ) and MPM ( Metra Potential Method ).
literature
- Manfred Schulte-Zurhausen : Organization. Vahlen, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-8006-3205-5
- Reinhard Haberfellner, Walter F. Daenzer (eds.), Mario Becker: Systems Engineering . Methodology and practice. Industrielle Organization Verlag, Zurich 1997, ISBN 3-85743-973-4 , p. 562