North African gerbil: Difference between revisions
Tom.Reding (talk | contribs) m +Category:Taxonomy articles created by Polbot; cleanup; WP:GenFixes on, using AWB |
SimLibrarian (talk | contribs) m add navbox that links here, periods only for complete-sentence image captions (MOS:CAPFRAG), capitalization edits |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Species of rodent}} |
|||
{{speciesbox |
|||
{{Speciesbox |
|||
| name = North African gerbil<br/>''Dipodillus campestris'' |
|||
| image = Dipodillus campestris - North African Gerbil.jpg |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| image_caption = ''Dipodillus campestris'', Tiguentourine gas field, In Amenas, Algeria |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
||
| status_ref= <ref name=IUCN>{{ |
| status_ref = <ref name=IUCN>{{cite iucn |author=Granjon, L. |year=2016 |title=''Gerbillus campestris'' |page=e.T45088A22465830 |doi=10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T45088A22465830.en |access-date=13 March 2022}}</ref> |
||
| genus = Dipodillus |
| genus = Dipodillus |
||
| species = campestris |
| species = campestris |
||
| authority = (Levaillant, 1857)<ref>ITIS (2020). ITIS: The Integrated Taxonomic Information System (version 2020-10-28). In: Roskov Y., Ower G., Orrell T., Nicolson D., Bailly N., Kirk P. M., Bourgoin T., DeWalt R. E., Decock W., van Nieukerken E. J., Penev L. (eds.). ''Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life'', 2020-12-01. Digital resource at https://www.catalogueoflife.org/. Species 2000: Naturalis, Leiden, the Netherlands. ISSN 2405-8858.</ref> |
|||
| authority = ([[Victor Loche|Loche]], 1867) |
|||
| range_map = Gerbillus campestris distribution.png |
| range_map = Gerbillus campestris distribution.png |
||
| synonyms = |
| synonyms = ''Gerbillus campestris'' (Loche, 1867)<br /> |
||
''Gerbillus campestris'' (Loche, 1867)<br> |
|||
'''''quadrimaculatus''''' (Lataste, 1882) |
'''''quadrimaculatus''''' (Lataste, 1882) |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''North African gerbil''' (''Dipodillus campestris'') is a species of [[rodent]] in the family [[Muridae]]. It is found in North Africa where its natural [[habitat]]s are [[arable land]] and rocky areas of the [[Maghreb]], and hot [[Sahara]]n [[desert]]s. |
The '''North African gerbil''' ('''''Dipodillus campestris''''') is a species of [[rodent]] in the family [[Muridae]]. It is found in North Africa where its natural [[habitat]]s are [[arable land]] and rocky areas of the [[Maghreb]], and hot [[Sahara]]n [[desert]]s. |
||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
The North African gerbil has long soft fur and a relatively long tail. The dorsal fur is cinnamon to orange-brown. Each hair has a grey base, a sandy or golden-brown terminal section and often a black tip. The cheeks and throat are white and there is sometimes a dark stripe on the nose. The underparts are white, with a clear division between the dorsal and ventral colours. The legs and feet are white and the soles of the feet are bare. The tail is |
The North African gerbil has long soft fur and a relatively long tail. The dorsal fur is cinnamon to orange-brown. Each hair has a grey base, a sandy or golden-brown terminal section and often a black tip. The cheeks and throat are white and there is sometimes a dark stripe on the nose. The underparts are white, with a clear division between the dorsal and ventral colours. The legs and feet are white and the soles of the feet are bare. The tail is almost twice the length of the head-and-body, and is bicoloured, golden-brown above and white below. The tip of the tail forms a pencil, a tuft of longer hair.<ref name=Kingdon>{{cite book|author1=Jonathan Kingdon|author2=David Happold|author3=Thomas Butynski|author4=Michael Hoffmann|author5=Meredith Happold|author6=Jan Kalina|title=Mammals of Africa|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=B_07noCPc4kC&pg=RA2-PA302 |year=2013|publisher=A&C Black|isbn=978-1-4081-8996-2 |pages=302–303}}</ref> |
||
==Distribution and habitat== |
==Distribution and habitat== |
||
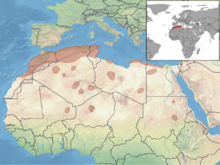
The North African gerbil is found in [[Algeria]], [[Egypt]], [[Libya]], [[Mali]], [[Morocco]], [[Niger]], [[Sudan]], [[Tunisia]], and possibly [[Chad]] and [[Mauritania]].<ref name=IUCN/> Its habitat varies across its range, but in general it favours habitats with rocks and vegetation rather than sand.<ref name=Kingdon/> |
The North African gerbil is found in [[Algeria]], [[Egypt]], [[Libya]], [[Mali]], [[Morocco]], [[Niger]], [[Sudan]], [[Tunisia]], and possibly [[Chad]] and [[Mauritania]].<ref name=IUCN/> Its habitat varies across its range, but in general it favours habitats with rocks and vegetation rather than sand and gravel .<ref name=Kingdon/> |
||
==Ecology== |
==Ecology== |
||
The North African gerbil lives in a burrow that it digs and is a terrestrial and nocturnal |
The North African gerbil lives in a burrow that it digs and is a terrestrial and nocturnal animal. The timing of breeding depends on location, but in Egypt coincides with the winter rains, and in North Sudan follows the short wet season in September to November. The litter size is about five pups. The diet of this rodent has not been studied.<ref name=Kingdon/> |
||
The North African gerbil, part of the rodent family, is often considered a pest within its natural habitat. Erosion, urbanization, and agriculture are some of the most prominent threats to the North African gerbil and other African rodents. As a burrowing rodent, farmers often aim to harm North African gerbils as they pose threats to crop yields.<ref>AMR, ZUHAIR S. et al. Systematics, distribution and ecological analysis of rodents in Jordan. Zootaxa, [S.l.], v. 4397, n. 1, p. 1–94, mar. 2018. ISSN 1175-5334. Date accessed: 4 March 2020. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4397.1.1. |
|||
</ref> |
|||
==Status== |
==Status== |
||
| Line 30: | Line 33: | ||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
*{{MSW3 Muroidea | id = 13001061 | page = 1214}} |
*{{MSW3 Muroidea | id = 13001061 | page = 1214}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Dipodillus]] |
[[Category:Dipodillus]] |
||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Mammals of West Africa]] |
[[Category:Mammals of West Africa]] |
||
[[Category:Mammals of Sudan]] |
[[Category:Mammals of Sudan]] |
||
[[Category:Mammals of North Africa]] |
|||
[[Category:Mammals described in 1867]] |
[[Category:Mammals described in 1867]] |
||
[[Category:Taxa named by Victor Loche]] |
|||
[[Category:Maghreb]] |
[[Category:Maghreb]] |
||
[[Category:Taxonomy articles created by Polbot]] |
[[Category:Taxonomy articles created by Polbot]] |
||
[[Category:Taxobox binomials not recognized by IUCN]] <!-- Dipodillus campestris --> |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:16, 12 February 2024
| North African gerbil | |
|---|---|

| |
| Dipodillus campestris, Tiguentourine gas field, In Amenas, Algeria | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Genus: | Dipodillus |
| Species: | D. campestris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dipodillus campestris (Levaillant, 1857)[2]
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Gerbillus campestris (Loche, 1867) | |
The North African gerbil (Dipodillus campestris) is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in North Africa where its natural habitats are arable land and rocky areas of the Maghreb, and hot Saharan deserts.
Description[edit]
The North African gerbil has long soft fur and a relatively long tail. The dorsal fur is cinnamon to orange-brown. Each hair has a grey base, a sandy or golden-brown terminal section and often a black tip. The cheeks and throat are white and there is sometimes a dark stripe on the nose. The underparts are white, with a clear division between the dorsal and ventral colours. The legs and feet are white and the soles of the feet are bare. The tail is almost twice the length of the head-and-body, and is bicoloured, golden-brown above and white below. The tip of the tail forms a pencil, a tuft of longer hair.[3]
Distribution and habitat[edit]
The North African gerbil is found in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and possibly Chad and Mauritania.[1] Its habitat varies across its range, but in general it favours habitats with rocks and vegetation rather than sand and gravel .[3]
Ecology[edit]
The North African gerbil lives in a burrow that it digs and is a terrestrial and nocturnal animal. The timing of breeding depends on location, but in Egypt coincides with the winter rains, and in North Sudan follows the short wet season in September to November. The litter size is about five pups. The diet of this rodent has not been studied.[3] The North African gerbil, part of the rodent family, is often considered a pest within its natural habitat. Erosion, urbanization, and agriculture are some of the most prominent threats to the North African gerbil and other African rodents. As a burrowing rodent, farmers often aim to harm North African gerbils as they pose threats to crop yields.[4]
Status[edit]
The North African gerbil is a common species that flourishes in a range of different environments and in some locations, such as in Morocco, it is reckoned to be an agricultural pest species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the conservation status of this rodent as being of "least concern".[1]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Granjon, L. (2016). "Gerbillus campestris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T45088A22465830. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T45088A22465830.en. Retrieved 13 March 2022.
- ^ ITIS (2020). ITIS: The Integrated Taxonomic Information System (version 2020-10-28). In: Roskov Y., Ower G., Orrell T., Nicolson D., Bailly N., Kirk P. M., Bourgoin T., DeWalt R. E., Decock W., van Nieukerken E. J., Penev L. (eds.). Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life, 2020-12-01. Digital resource at https://www.catalogueoflife.org/. Species 2000: Naturalis, Leiden, the Netherlands. ISSN 2405-8858.
- ^ a b c Jonathan Kingdon; David Happold; Thomas Butynski; Michael Hoffmann; Meredith Happold; Jan Kalina (2013). Mammals of Africa. A&C Black. pp. 302–303. ISBN 978-1-4081-8996-2.
- ^ AMR, ZUHAIR S. et al. Systematics, distribution and ecological analysis of rodents in Jordan. Zootaxa, [S.l.], v. 4397, n. 1, p. 1–94, mar. 2018. ISSN 1175-5334. Date accessed: 4 March 2020. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4397.1.1.
- Musser, G.G.; Carleton, M.D. (2005). "Superfamily Muroidea". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 1214. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.

