Vicianose
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (May 2014) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
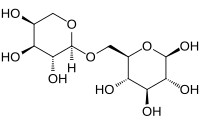
| IUPAC name
(3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3,4,5-Trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol
| |
| Other names
6-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-D-glucopyranose
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H20O10 | |
| Molar mass | 312.271 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Vicianose is a disaccharide.
Vicianin is a cyanogenic glycoside containing vicianose. The enzyme vicianin beta-glucosidase uses (R)-vicianin and water to produce mandelonitrile and vicianose.
The fruits of Viburnum dentatum appear blue. One of the major pigments is cyanidin 3-vicianoside, but the total mixture is very complex.[1]
References[edit]
- ^ F.J. Francis and Pericles C. Markakis (1989). "Food colorants: Anthocyanins". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 28 (4): 273–314. doi:10.1080/10408398909527503. PMID 2690857.
