2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase
| 2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase | ||
|---|---|---|
| other names |
|
|
| Cofactor | NAD + | |
| Enzyme Classifications | ||
| EC, category | 1.1.1.98 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | Dehydration | |
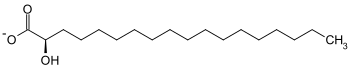
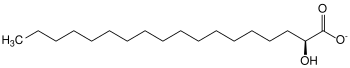
| Substrate | ( R ) -2-hydroxystearate + NAD + | |
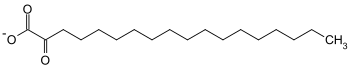
| Products | 2-oxostearate + NADH + H + | |
| EC, category | 1.1.1.99 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | Dehydration | |
| Substrate | ( S ) -2-hydroxystearate + NAD + | |
| Products | 2-oxostearate + NADH + H + | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Eukaryotes | |
2-Hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenases (also 2-hydroxy fatty acid oxidases ) are enzymes that catalyze the dehydrogenation of 2-hydroxystearate to 2-oxostearate . These enzymes belong to the family of oxidoreductases , with the hydroxyl group acting as a donor and NAD + as an acceptor . A distinction is made between ( R ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase and ( S ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase.
The ( R ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase must not be confused with the D -2-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase (also known as D- lactate dehydrogenase , EC 1.1.99.6).
properties
Above all, the ( R ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase is used for the stereospecific reduction of 2-ketocarboxylic acids to D -2-hydroxycarboxylic acids . The enzyme takes part in β-oxidation . ( R ) -2-Hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase is of physiological importance, since 2-hydroxy fatty acids are naturally in the ( R ) configuration . It has also been shown that 2-hydroxypalmitate is formed from the degradation of phytosphingosine in the liver. The ( S ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase probably takes part in the α-oxidation in the degradation of natural and / or branched long-chain fatty acids. ( S ) -2-Hydroxy fatty acids occur as intermediates in the α-oxidation of natural fatty acids in plants. The activity of these oxidoreductases is reduced by the lack of NAD + and also depends on reduced pyridine nucleotides .
Catalytic equilibria
( R ) -2-Hydroxystearate is oxidized and dehydrated by ( R ) -2-Hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase. In addition to the reduction equivalent NADH , 2-oxostearate is formed. This reaction is important for fatty acid oxidation .
( S ) -2-hydroxystearate is oxidized and dehydrated by the ( S ) -2-hydroxy fatty acid dehydrogenase. In addition to the reduction equivalent NADH, 2-oxostearate is formed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Patent EP0130288 : Microbiologically prepared d-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic-acid dehydrogenase, process for its production and its use. Published on March 2nd, 1988 , inventors: Wolfgang Leuchtenberger, Werner Hummer, Maria-Regina Kula, Horst Schütte.
- ^ S. Gatt, Y. Barenholz: Degradation of sphingosine bases by cell-free preparations. Alpha-hydroxy palmitic acid, an intermediate of phytosphingosine degradation. In: Biochemical and biophysical research communications. Volume 32, Number 4, August 21, 1968, pp. 588-594, doi : 10.1016 / 0006-291x (68) 90277-5 , PMID 5682281 .
- ↑ JF Mead, GM Levis: A 1 carbon degradation of the long chain fatty acids of brain sphingolipids. In: Journal of Biological Chemistry . Volume 238, May 1963, pp. 1634-1636, PMID 13934294 .
- ^ SC Tsai, JH Herndon, BW Uhlendorf, HM Fales, CE Mize: The formation of alpha-hydroxy phytanic acid from phytanic acid in mammalian tissues. In: Biochemical and biophysical research communications. Volume 28, Number 4, August 1967, pp. 571-577, doi : 10.1016 / 0006-291x (67) 90352-x , PMID 6052492 .
- ^ LJ Morris, C. Hitchcock: The stereochemistry of alpha-oxidation of fatty acids in plants. The stereochemistry of biosynthesis of long-chain 2-hydroxyacids. In: European Journal of Biochemistry . Volume 4, Number 2, April 3, 1968, pp. 146-148, doi : 10.1111 / j.1432-1033.1968.tb00185.x , PMID 5655491 .
- ↑ Gabriel M. Levis: 2-Hydroxy fatty acid oxidases of rat kidney . In: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications . 38, No. 3, February 6, 1970, pp. 470-477. doi : 10.1016 / 0006-291X (70) 90737-0 . PMID 5443694 .