Aldol condensation
The aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in the field of organic chemistry . During the reaction, aldehydes and ketones form α, β- unsaturated carbonyl compounds , more precisely α, β-unsaturated aldehydes or ketones, with elimination of water .
Overview reaction
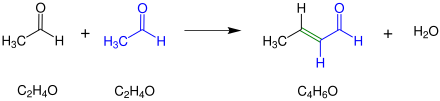
The aldol condensation can take place with either acid or base catalysis. The aldol condensation is explained here using the reaction of two acetaldehyde molecules as an example .
The double bond marked in green shows the newly made double bond that is formed during the aldol condensation.
The reaction produces an α, β-unsaturated aldehyde with elimination of water .
mechanism
The base- and acid-catalyzed mechanisms of aldol condensation are explained using the example of the reaction of two acetaldehydes.
Base-catalyzed aldol condensation
In the following, the mechanism of the base-catalyzed aldol condensation is presented using the above example:
Mechanism of the base-catalyzed condensation.
In aldol condensation, as in aldol addition, 3-hydroxybutanal ( 2 ), i.e. an aldol , is initially formed from acetaldehyde ( 1 ) via a few intermediate stages . This is followed by the deprotonation of an acidic hydrogen atom by a base. A C = C double bond is formed and a hydroxide ion is released as a leaving group . The result is trans -2-butenal ( 3 ).
Acid-catalyzed aldol condensation
In the following, the mechanism of the acid-catalyzed aldol condensation is also presented using the example above:
Mechanism of acid-catalyzed condensation.
Here, too, aldol 2 is initially formed from acetaldehyde ( 1 ) via intermediate stages . In an acidic environment, this tautomerizes to cis -but-1-ene-1,3-diol ( 4 ). This is protonated to the oxonium ion 5 and water is split off by rearrangement of electron pairs . Finally, a proton is split off from the oxonium ion 6 and crotonaldehyde is formed ( 7 ).
See also
literature
- KPC Vollhardt , NE Schore: Organic Chemistry . 4th edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005 , ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 .
- J. Buddrus, B. Schmidt: Fundamentals of organic chemistry . 4th revised and updated edition, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2011 , ISBN 978-3-11-024894-4 .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b J. Buddrus, B. Schmidt: Fundamentals of organic chemistry . 4th revised and updated edition, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2011 , ISBN 978-3-11-024894-4 , p. 616 ff.