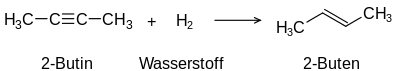Unsaturated compounds
| Unsaturated compounds | |
|---|---|
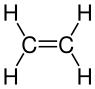 Ethene |
Ethine |
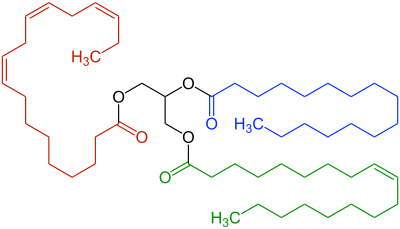
 α-linolenic acid |
|
As Unsaturated compounds is called organic chemical compounds whose molecular structure one or more carbon-carbon double or triple bonds contains. These can also be conjugated . Examples are the unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated hydrocarbons ( alkenes and alkynes ). Many natural substances are unsaturated compounds. In contrast, saturated compounds are those organic-chemical compounds in which all bonds between carbon atoms are CC single bonds .
History and characteristics
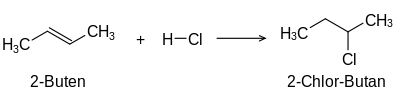
The term unsaturated compounds , originally unsaturated hydrocarbons , is derived from their ability to carry out typical addition reactions which are not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes :
This is where the only formally unsaturated aromatics differ from the other unsaturated compounds: Due to the high stability of the aromatic system, they do not carry out the typical addition reactions or only under extreme conditions such as high temperature or high pressure. Instead, substitution reactions are preferred.
properties
Unsaturated compounds are generally more reactive than saturated compounds. Triglycerides ( rapeseed oil , linseed oil , olive oil, etc.) with a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acid residues go rancid faster than those with a high proportion of saturated fatty acid residues, e.g. B. in coconut oil .
In addition, the melting point is significantly lower than that of fats with predominantly saturated fatty acids, which is why they are mostly liquid at room temperature and are therefore also referred to as fatty oils .
Examples
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
- Alkenes , polyenes , terpenes
- Alkynes
- Only formally unsaturated: aromatics such as benzene , naphthalene etc.
Unsaturated alcohols , aldehydes , ketones , carboxylic acids and esters
- Ascorbic acid , acetylformoin , bombycol , retinol
- Citronellal , Crotonaldehyde , E160e , Furfural , Retinal , Safranal
- Abscisic acid , anthrone , cyclohexenone
- unsaturated fatty acids
- lots of fats
Individual evidence
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd revised edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 , pp. 653-654.