Citronellal
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
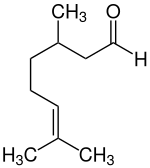
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Citronellal | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a fruity odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 154.25 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.85 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
208 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.451 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Citronellal , also Rhodinal (stress on the final syllable: Citronell a l , Rhodin a l ) is a clear, viscous liquid. It is a monoterpene - aldehyde .
Isomerism
Citronellal occurs in the form of two enantiomers , the ( R ) - (+) - citronellal [also called (+) - citronellal for short] and the ( S ) - (-) - citronellal [also called (-) - citronellal for short ]. A 1: 1 mixture of the racemate of both enantiomers is called ( RS ) - (±) -citronellal .
| Isomers of citronellal | ||||
| Surname | ( R ) -Citronellal | ( S ) -Citronellal | ||
| other names | (+) - Citronellal | (-) - Citronellal | ||
| Structural formula |
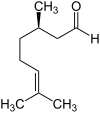
|
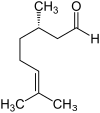
|
||
| CAS number | 2385-77-5 | 5949-05-3 | ||
| EC number | 219-194-5 | 227-707-9 | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.017.450 | 100.025.189 | ||
| PubChem | 75427 | 443157 | ||
| Wikidata | Q413787 | Q27105293 | ||
The compound with a terminal double bond is referred to as α-citronellal .
Occurrence
( R ) -Citronellal is found mainly in citrus plants and in citronell oil . The oil from the leaves of the lemon contains between 25,000 and 89,000 ppm , the fruit of the lime about 140 and the fruits of the juniper about 160 ppm ( R ) -citronellal. ( S ) -Citronellal is the main component of the essential oil of the kaffir lime leaves with around 80% .
Extraction and presentation
Citronellal can be made from pine trees . β-pinene is transformed into myrcene at temperatures above 500 ° C. Myrcene reacts with diethylamine and butyllithium . The resulting chelate reacts to N , N -diethylgeranylamine, which is rearranged on a special catalyst to (3 r ) -1 E -1-diethylamino-3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadiene. This is hydrolyzed to citronellal .
The heterogeneously catalyzed hydrogenation of citral in the presence of palladium catalysts normally only leads to dihydrocitronellal with citronellal as an intermediate stage. In the presence of ionic liquids based on nitrile-functionalized imidazolium salts , the second hydrogenation step can be suppressed and thus citronellal can be obtained as the main product.
properties
The liquid boils at a normal pressure of 101.3 kilopascals at about 208 ° C. The density is about 0.85 g · cm −3 . It is readily soluble in ethanol , but hardly in water and glycerine . The molar mass is 154.25 g mol −1 . The flash point is 78 ° C.
use
Citronellal is also used as a starting material for the synthesis of (1 R , 3 R , 4 S ) - (-) - menthol . It first forms a chelate with zinc bromide , which is converted into isopulegol , which is then hydrogenated to menthol. It is also used to produce hydroxycitronellal , to which it can react in the presence of water .
It is used in cheap fragrances, also to perfume cigarettes and as an insect repellent ( repellent ).
The non-naturally occurring cannabinoid hexahydrocannabinol (HHM) can be synthesized stereoselectively by condensation with 5- n -pentyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione followed by a Diels-Alder reaction . The ( R ) - epimer of HHM is as active as the Δ⁸-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ⁸-THC), but in contrast to Δ 9 -THC, cannabis only contains small amounts.
Risk assessment
Citronellal was included by the EU in 2014 in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of the substance evaluation in the Community's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ). The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. Citronellal uptake was caused by concerns about consumer use , worker exposure , high (aggregated) tonnage and widespread use, as well as the suspected dangers of sensitizing properties. The re-evaluation took place from 2015 and was carried out by Sweden . A final report was then published.
Web links
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on citronellal in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet (±) -Citronellal from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 23, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links for α-citronellal : CAS number: 141-26-4, EC number: 205-474-4, ECHA InfoCard: 100.004.978 , PubChem : 101628 , Wikidata : Q27273446 .
- ↑ P. Claus, J. Arras, D. Ruppert: Influence of ionic liquids with functionalized cations on the palladium-catalyzed liquid-phase hydrogenation of citral , in: Chem. Ing. Techn. , 2009 , 81 , pp. 2007-2011; doi : 10.1002 / cite.200900085 .
- ↑ Tietze, L.-F., von Kiedrowski, G. and Berger, B. (1982), Stereo- and Regioselective Synthesis of Enantiomerically Pure (+) - and (-) - Hexahydrocannabinol by Intramolecular Cycloaddition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 21: 221-222. doi : 10.1002 / anie.198202212
- ↑ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Conclusion and Evaluation Report .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Citronellal , accessed on March 26, 2019.



