Diethylamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
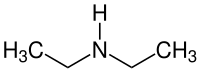
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diethylamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 11 N | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, highly flammable liquid with an amine-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 73.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.71 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−50 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
56 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
10.98 (protonated) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
completely miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3864 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 5 ml m −3 or 15 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Diethylamine is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic secondary amines .
Extraction and presentation
Diethylamine can be obtained by reacting ethanol with ammonia , which also results in ethylamine and triethylamine .
properties
The aqueous solution of diethylamine has a strongly alkaline reaction . Diethylamine decomposes from around 500 ° C. It has a dynamic viscosity of 0.34 mPas at 25 ° C.
Safety characteristics
Diethylamine forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures with air. The compound has a flash point below −20 ° C. The explosion range lies between 1.7% by volume (50 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 10.1% by volume (305 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The limit gap width was determined to be 1.15 mm (50 ° C). This results in an assignment to explosion group IIA. The ignition temperature is 305 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2.
use
Diethylamine is used in the production of rubber , textile and flotation chemicals , synthetic resins, dyes and pharmaceuticals, insecticides , galvanic baths and polymerization retarders, and as a pH value regulator and buffer substance. It can also be used to make the neurotoxin tabun .
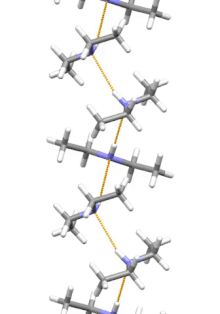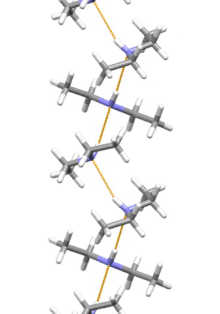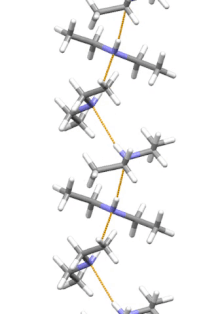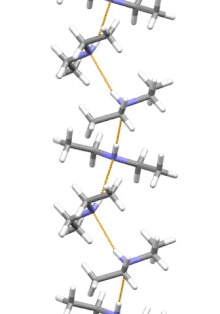
Supramolecular structure
Diethylamine is the smallest and simplest molecule that has a supramolecular helix as an aggregate with the lowest energy. Other similarly small hydrogen-bonded molecules prefer cyclic structures.
Related and derived links
- Diethylamine hydrochloride (diethylammonium chloride), C 4 H 12 ClN
- Diethylamine hydrobromide , C 4 H 12 BrN
- N , N -diethylaniline , C 10 H 15 N
- N - (trimethylsilyl) diethylamine , C 7 H 19 NSi
- Diethylamine Salicylate , C 11 H 17 NO 3
- Diethylammonium acetate , C 6 H 15 NO 2
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Entry on diethylamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 26, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ HK Hall: Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79, 1957, p. 5441, doi : 10.1021 / ja01577a030 .
- ↑ Steven Pedersen: Understanding the Principles of Organic Chemistry: A Laboratory Course. Cengage Learning, 2010, ISBN 978-0-495-82993-5 , p. 23 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c data sheet diethylamine (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 21, 2011.
- ↑ Entry on Diethylamine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values , accessed on August 28, 2019.
- ↑ a b c Sorbe - Safety-related characteristics of chemical substances, 131. Supplementary delivery 8/2009, ecomed-Verlag.
- ^ Robert Turkington: Chemicals Used for Illegal Purposes . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-18780-7 , pp. 324 ( books.google.de ).
- ↑ Felix Hanke, Chloe J. Pugh, Ellis F. Kay, Joshua B. Taylor, Stephen M. Todd, Craig M. Robertson, Benjamin J. Slater, Alexander Steiner: The simplest supramolecular helix . In: Chemical Communications . tape 54 , 2018, doi : 10.1039 / C8CC03295E .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for diethylammonium bromide: CAS number: 6274-12-0, EC number: 228-466-2, ECHA InfoCard: 100.025.879 , Wikidata : Q82860734 .
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to N- (trimethylsilyl) diethylamine : CAS number: 996-50-9, EC number: 213-637-6, ECHA InfoCard: 100.012.397 , PubChem : 70454 , ChemSpider : 63633 , Wikidata : Q3869305 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to diethylamine salicylate: CAS number: 4419-92-5, EC number: 224-586-4, ECHA InfoCard: 100.022.353 , PubChem : 9837223 , ChemSpider : 19278 , Wikidata : Q27262917 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for diethylammonium acetate: CAS number: 20726-63-0, EC number: 243-990-1, ECHA InfoCard: 100.039.976 , Wikidata : Q81993222 .