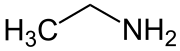
Ethylamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethylamine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 7 N | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas with a pungent, amine-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 45.08 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.162 g m −3 (0 ° C, 1013 mbar) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−81 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
16.6 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
10.75 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Can be mixed as required in water , ethanol and diethyl ether |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3663 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−47.5 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Ethylamine (according to IUPAC nomenclature : ethanamine , often also referred to as aminoethane ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of aliphatic primary amines . It is sold as a 50 or 70% aqueous solution . Ethylamine is an important intermediate in the chemical industry .
Extraction and presentation
The large-scale production of ethylamine takes place by reacting ethanol with ammonia at temperatures of 180-220 ° C and pressures of 20-70 bar in the presence of hydrogen over a copper , nickel or cobalt-containing catalyst , which is supported with metal oxides such as silicon dioxide or aluminum oxide is. The complete reaction preferably takes place in the gas phase in tube or tube bundle reactors . The catalyst is arranged as a fixed bed .
As by-products in addition to water also diethylamine and triethylamine formed by multistage distillation under pressure in the rectification columns have to be separated. Instead of conventional ethanol, preference is given to using so-called bioethanol , which was obtained through biotechnological fermentation .
Ethylamine can also be made by the catalytic hydrogenation of acetonitrile , acetamide, or nitroethane . Furthermore, the reaction of ethene with ammonia with base catalysis (e.g. sodium amide ) also produces ethylamine. In addition, ethylamine can be synthesized by the nucleophilic substitution of haloethanes (such as chloroethane or bromoethane ) with ammonia using a strong base such as potassium hydroxide . However, these processes are not economical and are therefore not used on an industrial scale.
properties
Physical Properties
Ethylamine has a melting point of −81 ° C and a boiling point of 16.6 ° C. The critical temperature is 183.4 ° C, the critical pressure 56.3 bar and the critical density 0.248 g / cm³. The flash point is -37 ° C and the ignition temperature is 385 ° C. At 20 ° C, ethylamine has a vapor pressure of 1.144 bar.
Chemical properties
Ethylamine belongs to the group of aliphatic amines and is a colorless gas with an amine-like odor at room temperature . The extremely flammable gas forms explosive mixtures with air and is heavier than air. It dissolves in water with hydrolysis . The solutions of ethylamine are strongly alkaline . This substance also poses acute or chronic health risks. Reaction with other substances can lead to the formation of nitrous gases . Ethylamine acts as an initiator on various polymerizable substances .
use
Ethylamine is a versatile intermediate in the chemical industry with various possible uses. The main application of ethylamine is its further processing into plant protection products (e.g. atrazine and simazine ). Monoethylamine is also used in the production of mining chemicals such as flotation agents (e.g. isopropyl ethyl thiocarbamate) and in the production of polyurethane foams as a chain stopper to control the polymerisation process . It is the starting material for the synthesis of dyes , pharmaceuticals and herbicides .
safety instructions
Ethylamine is an extremely flammable gas which forms explosive mixtures with air. It is mainly absorbed through the respiratory tract . Furthermore, good absorption via the mucous membranes and the skin is assumed. After uptake of the gas, a strongly irritating to corrosive effect on the mucous membranes and skin is to be expected, chronic irritative effects on the mucous membranes and disturbances of the general condition can occur. Reproductive toxicity , mutagenicity and carcinogenicity have not been confirmed in tests, but ethylamine can react with other substances to form carcinogenic compounds. Ethylamine has a lower explosion limit of 3.50% by volume at 65 g · cm −3 and an upper explosion limit of 14.0% by volume at 260 g · cm −3 . The ignition temperature is 385 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2. With a flash point of −37 ° C, ethylamine is extremely flammable.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on ethylamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 6, 2018.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry on ethylamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 6, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut: Amines, Aliphatic . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2000, ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2 , doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a02_001 .
- ↑ Entry on Ethylamine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values , accessed on August 28, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ a b Norbert Asprion, Manfred Julius, Oliver Bey, Stefanie Werland, Frank Stein, Matthias Kummer, Wolfgang Mägerlein, Johann-Peter Melder, Kevin Huyghe, Maarten Moors: Process for the production of ethylamines and mono-iso-propylamine (MIPA). In: Google Patents. BASF SE, October 21, 2015, accessed April 8, 2019 .
- ^ BASF SE: Ethylamine. In: BASF product search. BASF SE, accessed December 6, 2018 .


