Flotation
Flotation (from English to float - to swim) is a physical-chemical separation process for fine-grained solids due to the different surface wettability of the particles. The process takes place in a liquid, often water, and with a supply of gas, often air.
According to the definition in accordance with VDMA standard sheet 24430, this is a separation process in which substances dispersed or suspended in water are transported to the surface of the water by adhering gas bubbles and removed there with a clearing device.
Working principle
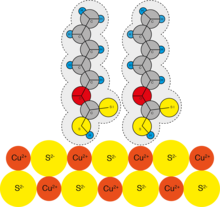
Flotation takes advantage of the fact that gas bubbles easily attach to hydrophobic , i.e. H. Adhere to surfaces that are difficult to wet by water and give the particles buoyancy so that they float.
The prerequisite is that the gas used is difficult to dissolve in water . Under these conditions, the hydrophobic gas bubbles collect on the hydrophobic particle surfaces.
Auxiliary materials
Various auxiliary substances are used in flotation :
- Collectors are critical to the effectiveness of the process. They make the proportion of the mixture to be applied in the foam water-repellent (hydrophobic), while the other components should remain water-attracting ( hydrophilic ). Air blown into the slurry adheres only to the hydrophobic particles and carries them to the water surface, while the hydrophilic particles remain in the turbidity. Certain sulfur compounds (such as xanthates , dithiophosphates, mercaptans ), amines , alkyl sulfonates and some fatty acid salts are suitable as collectors .
- Foamers are used to stabilize the air bubbles.
- Push-buttons improve the wettability (hydrophilicity) and accelerate the sinking in the separating medium.
- Regulators such as pH regulators , flocculants and others are used to optimize and selectively separate ore mixes .
Relaxation flotation
The relaxation flotation makes use of Henry - Dalton's law that the solubility of a gas in a liquid phase at constant temperature increases proportionally with the partial pressure of this gas above the liquid. If you put water under pressure, saturate it with gas or air and then bring the water back to ambient pressure ("relaxation"), a corresponding proportion of gas or air is released in the form of very fine bubbles. The bubble size depends on the operating conditions, but is generally less than 100 μm .
The bubble size after relaxation depends on the design of the relaxation organ, among other things, on the pressure difference, the surface tension , the pH value , the salt concentration and the viscosity of the liquid.
The design of the air saturation and expansion elements differ depending on the provider of the flotation system.
There are three variants for generating the required fine gas bubbles:
- the full flow process , in which the entire feed is saturated with air
- the partial flow method in which only part of the feed is saturated with air
- the recycling process , in which any amount of the purified water is recirculated and thereby saturated with air.
The amount of air introduced in the full and partial flow process is limited, and accordingly the achievable separation efficiency. Another disadvantage is the risk of clogging and the high mechanical stress on the flakes in the saturation system. These disadvantages do not exist in
the recycling process . The amount of recirculation can be adapted so that the necessary number of fine gas bubbles is sufficient for all expected operating conditions.
Applications
In wastewater treatment
In wastewater technology and wastewater treatment , flotation is a separation process in which substances and particles dispersed or suspended in water are transported to the surface of the water by adhering gas bubbles with a diameter of less than 100 μm and removed there with a scraper device.
All flotation processes have in common that small gas bubbles are required to float the substances to be separated. The main differences between the individual processes lie in the type of bubble generation and, as a result, the quality, quantity and size of the bubbles.
The accumulation of air bubbles on solids takes place more easily or is more intense, the smaller the bubbles produced are. Due to the better accumulation of small bubbles, the reduction of the bubble size leads on the one hand to an improved utilization of the air introduced and also to a more complete expulsion of the solids from the wastewater, whereby both the solids concentration in the clear flow area of the flotation decreases, as well as the solids content in the flotate and the stability of the flotation cover increases.
In wastewater technology, the pressure release flotation or release flotation (English: Dissolved Air Flotation, abbreviated to DAF ) is by far the most widespread. Both in the municipal as well as industrial wastewater treatment, which has flotation proven to be most efficient and most economical method.
In ore processing
In mining, flotation is used as a treatment process to separate ore from waste rock. It has replaced traditional blow-down in most areas of application .
In ore processing, lead , zinc , fluorspar and copper ores are concentrated in an aqueous slurry ( suspension ) by flotation. The slurry ore pulp or English slurry called, rarely, ore pulp or ore slurry . Fine grinding is necessary for this process in order to sufficiently break down the ore contained. The suspension is fed to the flotation bath in the flotation cell.
Air is fed into the flotation bath by a high-speed stirrer or lance and finely distributed. The surfactants and foam stabilizers contained in the flotation bath stabilize the air bubbles. The mineral granules hydrophobized with a collector are more difficult to wet with water and therefore adhere better to finely divided air bubbles. These particles float with the air bubbles and can be skimmed off with the foam stabilized by the foamer. The remaining particles (gangue) should remain in the sludge and are pumped out at the end of the flotation process.
Often several flotation cells are coupled one behind the other to form flotation banks, so that an ore concentrate with a higher metal content is created.
Coal flotation
Coal flotation is a process for processing hard coal. Since the ground coal particles have a lower specific weight than water, they float in the flotation bath. Coal tar oils can be used as foaming agents . The coal is skimmed off in the foam and discharged.
Separation of crystals
Other substances such as potassium chloride crystals can also be enriched through flotation.
In paper recycling
Flotation is an important process step in paper recycling in Europe. With the flotation, the whiteness of the waste paper used should be increased during deinking by removing the printing inks . This makes use of the fact that only the hydrophilic fibers are wetted by water, while the hydrophobic printing ink remains largely unwetted.
Deinking chemicals such as surfactants, sodium hydroxide and water glass are added to the water in the flotation apparatus. After air has been introduced, the printing ink particles to be separated attach to the air bubbles and then float as foam on the waste paper suspension. The foam is skimmed off or sucked off the surface ( skimming ). The process is then repeated several times.
In order for waste paper to be processed using this process, it must meet certain requirements. For example, the printing inks used cannot be removed from newspapers produced using flexographic printing . They therefore cause considerable problems when recycling. Even small amounts of such newspapers in the waste paper lead to an unacceptably poor degree of whiteness. The ink particles are too small and not hydrophobic, so flotation does not work with them. Pigmented inkjet inks, digital printing processes with liquid toner and UV offset inks and varnishes pose similar problems.
An alternative to flotation is washing , which is used even more frequently in North America, while in Europe the flotation process dominates. Both processes separate the printing ink more or less selectively from the waste paper stock in different ways. However, fewer fibers are lost during flotation (approx. 10 percent; during washing - depending on the ash content - 20 to 30 percent). That is why flotation is now also gaining importance in North America.
New deinking systems for processing waste paper for graphic paper work almost exclusively according to the flotation principle. In contrast, the laundry is mainly used in the production of hygiene papers (kitchen rolls, toilet paper ). Here, as far as possible, all fillers should be washed out so that only the soft, long paper fibers remain.
In the medicine
In medicine , flotation methods are used to detect parasite eggs in the feces.
Individual evidence
- ^ Flotation , Lexicon of Chemistry.
- ↑ P. Somasundaran: Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science . CRC Press, 2006, ISBN 978-0-8493-9606-9 , p. 1787.
- ↑ a b c d VDMA standard sheet 24430: Flotation plants . Ed .: VDMA. 2001.
- ↑ Hempel, D .: Flotation . WEKA specialist publisher for technical executives GmbH, Augsburg 1994.
- ↑ Flotation in ore processing , Lexicon of Geosciences
- ↑ Multi-stage flotation system with collector optimization
-
↑ Process for flotation of inferior coal:
Patent DE69309481 : Process for coal flotation. Applied on September 28, 1993 , published September 25, 1997 , Applicant: Fording Coal Ltd., Inventor: Colin Mckenny, Brian Raymond. - ↑ R. Spangenberg, Lutz Stäudel and H. Wöhrmann: Separation of sodium and potassium salts by flotation. In: Practice of the natural sciences - chemistry in school . 1979, 28, 9, pp. 238-243 ( PDF ).
- ↑ INGEDE press release of July 3, 2015, accessed on August 20, 2018: Cross- linked colors are difficult to remove when deinking
- ↑ Parasitological fecal examination - flotation method ( Memento of the original from June 17, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.