Acetylformoin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
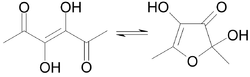
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetylformoin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 8 O 4 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Intense caramel-like smelling solid with a bitter taste |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 144.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Acetylformoin is a very reactive breakdown product of carbohydrates ( hexoses ) such as glucose . The substance is a diketo-enediol ( reductone ) with six carbon atoms, which z. B. arises as an intermediate product in the Maillard reaction and smells intensely of caramel .
presentation
The processes involved in the Maillard reaction are very complex and lead to melanoidins at sufficiently high temperatures , with acetylformoin being formed as a reactive intermediate. Formally, acetylformoin is formed by splitting off two water molecules from glucose via so-called deoxyosones :
When disaccharides react , structurally very similar, substituted derivatives of acetylformoin are formed.
properties
Acetylformoin can occur both in an open-chain form and, like the carbohydrates, in a cyclic "furenose" - hemiacetal form. The compound is very reactive and forms melanoidins such as pronyl-lysine during the further Maillard reaction with amino acids or proteins . More generally, aminohexose reductones or glycosylamines are formed . Acetylformoin itself has a bitter taste. The open-chain form has an intense smell of caramel, whereas the cyclic ketal form is odorless. In protic solvents such as water, the ring-shaped, non-odorous shape is formed immediately.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Wolfgang Engel: Odor-active compounds from the Maillard reaction of sulfur-free and sulfur-containing amine components with fructose ( Memento from September 28, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), German Research Institute for Food Chemistry , 1999.
- ↑ a b Kirsten Zeiter: New Methods for the Synthesis of Conformationally Restricted Peptidomimetics , September 11, 2001, Ludwig Maximilians University Munich .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c Anke Hollnagel: Contributions to the chemistry of non-enzymatic browning of oligomeric carbohydrates , TU Berlin , April 19, 2000 (PDF; 818 kB).
- ↑ Wolfgang Legrum: Fragrances, between stench and fragrance . Springer Fachmedien, Wiesbaden 2015, ISBN 978-3-658-07309-1 , p. 117 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-658-07310-7_5 .
- ^ German Research Institute for Food Chemistry : Annual Report ( Memento of September 28, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), 2001.
