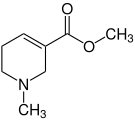
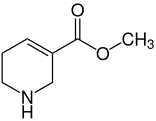
Areca alkaloids
Areca alkaloids are a collective name for the piperidine alkaloids of the betel nut, the seeds of the betel palm ( Areca catechu ).
Occurrence
The alkaloids of this group were isolated from the hemispherical seeds, about 3 cm in size, of the betel palm cultivated in India and East Asia.
Representative
The main alkaloid is arecoline , which makes up over 50% of the total alkaloid content. Further representatives are arecaidin , guvacolin and guvacin .
The total alkaloid content of the nuts increases with ripening and decreases again with subsequent drying. A roasting the dried nuts increases the proportion of the total alkaloid Arecolins.
properties
Arecoline is a powerful parasympathomimetic . It increases the secretion of saliva and sweat and stimulates the bowel movement. Areca preparations are now only used in veterinary medicine as wormers . Betel nuts are traditionally used as an aphrodisiac , anorectic , to stimulate digestion and as a diuretic , as well as in the treatment of asthma , cough , dermatitis , fainting , glaucoma , impotence , worm diseases , leprosy , toothache and vaginal discharge and to narrow the vagina .
The betel nuts are mainly in East Asia with some lime and leaves of Betelpfeffers chewed ( " betel ") and rain so much like tobacco, the nervous system.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e entry on Areca alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 17, 2020.
- ^ A b Vipin Jain, Apurva Garg, Mark Parascandola, Pankaj Chaturvedi, Samir S. Khariwala, Irina Stepanov: Analysis of Alkaloids in Areca Nut-Containing Products by Liquid Chromatography – Tandem Mass Spectrometry . In: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . tape 65 , no. 9 , February 28, 2017, p. 1977 , doi : 10.1021 / acs.jafc.6b05140 (English).
- ↑ a b H. R. Shwetha, VS Kotrashetti, N. Reddy, N. Chaitanya Babu: Estimation of the Major Constituents of Arecanut in Its Different Forms . In: Austin Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences . tape 7 , no. 1 , May 3, 2019, p. 1113 (English, org.sg [PDF]).
- ↑ Ashish Bhalla, Ponniah Thirumalaikolundusubramanian, Jeffery Fung, Gabriela Cordero-Schmidt, Sari Soghoian, Veronica Kaur Sikka, Harinder Singh Dhindsa, Surjit Singh: Native Medicines and Cardiovascular Toxicity . In: Meenakshisundaram Ramachandran (Ed.): Heart and Toxins . 1st edition. Academic Press, 2014, ISBN 978-0-12-416595-3 , chap. 6 , doi : 10.1016 / B978-0-12-416595-3.00006-2 (English).
- ↑ E. Breitmaier: Alkaloids . Springer Fachmedien, Wiesbaden 1997, ISBN 3-519-03542-1 , pp. 37 .