Arylamines
Arylamines or aromatic amines are built up from aromatic carbon rings that contain amino groups as substituents. They are chemically stable and have a basic character. They are moderately to poorly soluble in water and good in alcohol and fat solvents .
Representative
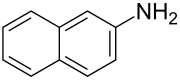
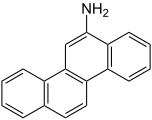
There are many different arylamines, which are divided into different groups based on their structure. For example, o -toluidine and 4-aminobiphenyl belong to the monocyclic arylamines, 2-naphthylamine and butter yellow belong to the bicyclic arylamines, and 6-aminochrysenic belong to the polycyclic arylamines. Further examples are p-phenylenediamine , 2,5-diaminotoluene and dimethylphenylenediamine .
Occurrence
With a few exceptions, they do not occur naturally, but are produced synthetically. These are then used as dyes , for plastic production and as antioxidants . Plus, they can also be found in tobacco smoke or hair dye .
metabolism
By absorption amines may be on the gastrointestinal tract are taken, the respiratory tract and rarely through the skin. After metabolism, it is mainly excreted via the kidneys. Most arylamines are completely eliminated after two to three days.
toxicology
The monocyclic and bicyclic arylamines are often toxic. This is due to their ability to produce methemoglobin . This ability is used for biomonitoring .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d entry on arylamines. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 16, 2020.