Automated property map
The automated real estate map ( ALK ; in Bavaria digital land map , DFK for short) is the digital successor to the analogue real estate map / land map, real estate map / city basemap and real estate map / appraisal map in the land registry offices in Germany.
The automated guided estate map provides as pictorial part together with the automated real estate book the (ALB) real estate register is.
history
With the specialist concept Automated Property Map ( ALK ), the Working Group of the Surveying Administrations of the Federal Republic of Germany (AdV) created a consistent concept for the automation of the verifications of the property map, the measurement and boundary points, the points of the basic survey and the measurement elements (angles, distances, etc.) that arise during property measurements. A completely new feature of this conception was the pronounced factual nature of the data modeling. Although the term automated property map suggests that computer graphics are being modeled here, the graphic form of the modeled data was only intended as an output form from the start . Instead, the data was modeled as technical objects according to the real world. With this approach, the concept made very high demands on the hardware and software available at the time.
The implementation was essentially carried out originally through the own programming of the surveying administrations of the federal states involved (in this case primarily Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia, with additional participation from Baden-Württemberg, Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate). Partial tasks were also assigned to well-known software companies (e.g. ADV / Orga, MBB, IABG). The main focus of the work was the ALK database part (implemented by Lower Saxony) and the ALK-GIAP (= graphically interactive workstation, implemented by North Rhine-Westphalia). Only later were corresponding software systems also offered by commercial companies. The ALK database part was only released for practical use in 1986 and initially only for the point data sub-area. The data for the measurement elements was not implemented because a cost-benefit study showed that it could not be used economically because of the high level of data required.
Data structure
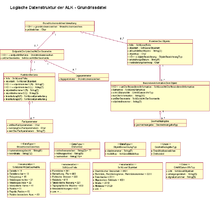
The data structure of the automated real estate map is defined by the logical data structure of the files of the ALK database part. All partial files (point file, floor plan file, attribute file, file of measurement elements, order book, etc.) have a hierarchical data structure. As an example, the logical data structure of the floor plan file is given here. The data structure was transferred from the original documentation to the UML data description language .
Data exchange
A standardized interface, the so-called EDBS (uniform database interface ), was developed for data exchange . When outputting to EDBS, the data structure of the partial file to be output is written in linearized form in a sequential text file. The automated real estate map should be replaced by 2010 together with the ALB as part of the automated real estate cadastre information system (ALKIS). However, this has not been done across the board.
Austria
In Austria the term digital cadastral map is used. It is available throughout Austria.
Poland
The property map is only partially available in an automated form. There are differences to the property register and land register. Until 2006, only 75 percent of the land was registered in the land register.
Web links
- The ALK page in GISWiki
- http://www.tim-online.nrw.de/
Individual evidence
- ↑ http://129.233.52.74/zeitschriftenartikel.jsp?z=2006089007145 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Property Security in Poland - Cadastre and Land Register, Journal of Geodesy, Geoinformation and Land Management, No. 4, 2006