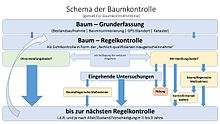
Tree cadastre
A tree register is a directory in which (city / street or park) trees are managed. The directory can be kept with paper forms or with the help of IT. All recorded trees must be clearly identified. In many tree registers, this is done using a tree number that is attached to the tree. However, digital tree registers in particular use GPS coordinates either additionally or exclusively for clear identification.
GIS- supported programs usually use high-quality GPS receivers to record the location, which is then entered directly into the geo-referenced maps to be provided. The high accuracy and GIS functions require extensive equipment. These systems are used by larger cities and municipalities as well as tree inspectors.
Server-supported programs or mobile phone applications roughly determine the location in order to correct the exact location using an aerial photo . These systems are used where there is no complex further processing in GIS and the tree location is determined by the tree inspector himself. The accuracy is sufficient for identification, but not for border disputes, which is why these systems are often used where tree control is the focus.
The following data is usually recorded in the tree register:
- Identification / designation of the tree (e.g. number, possibly with RFID )
- Associated facility ("Is part of green space facility nn")
- exact location (coordinates of the trees)
- Genus / tree species
- Planting year / age (if known)
- Status (e.g. natural monument )
- Photo of the tree (often)
- Risk assessment within the scope of the duty to maintain safety
- Responsibility, " owner " ( municipality , district , private, etc.)
- Date of the last inspection
- Date or month / year of the next inspection or inspection interval
- Document and photo references
The regular control is also documented in the tree register with the following entries:
- phase of development
- Condition data ( vitality assessment e.g. according to Roloff)
- Species protection notices, habitat structures
- Crown lock (condition)
- Description of the tree grate
- Tree height, trunk diameter (at chest height = 1.30 m) and crown diameter
- Abnormalities / defects in the crown area, trunk area, root neck and roots
- Pathogens
- Tree environment
- Recommended measures with priority
Every tree inspection must be concluded with a statement on the stability and breakage safety.
Since the tree owner (municipality, housing association, park administration, etc.) is responsible for road safety (including, for example, the stability of trees), tree registers are necessary tools to be able to carry out this task.
Modern tree registers often use pocket PCs with which the trees can be controlled. In addition to proving that there is a traffic safety obligation, tree registers also have the purpose of determining, writing out and documenting the tree care measures required for trees in the settlement area .
Germany
The requirements for tree control in Germany are ultimately given by the state of the art and by case law. The FLL Tree Control Guideline 2010 is a proposal for the regulation of tree control of individual trees and stands in Germany and was developed by the rules committee for traffic safety / tree controls taking into account relevant BGH judgments.
Basis of this guideline are
- Civil Code
- Federal Nature Conservation Act
- DIN 18920
- FLL ZTV -Baum-StB 04
- FLL ZTV Tree Care 2006
- FLL guidelines In-depth investigations
- FLL guideline for the valuation of protective and design greenery, nursery plants and permanent crops. Part A: Protection and design green
- FLL recommendations for tree planting - Part 1: Planning planting work, maintenance
- RAS-LP 4 Guideline for the construction of roads. Part landscape management, section 4: Protection of trees, vegetation and animals during construction work
The tree control directive would like to influence the state of the jurisprudence, means: It corresponds to the ideas of the above. Rules committee, but not the state of case law at all points (e.g. the control intervals are still the subject of intensive specialist discussions).
Tree registers can also be made available to the interested public. The cities of Hamburg, Frankfurt, Bonn, Leipzig, Berlin and Chemnitz have free tree registers under Open Data license.
Austria
ÖNORM L 1122: 2011 (guidelines for tree control and tree care) is to be used for tree control and tree care of individual trees and forest-like stands. It contains instructions for the creation of specifications. This ÖNORM does not apply to forest areas according to the Austrian Forest Act 1975. In Austria, ÖNORM L 1122: 2011 is also relevant for the management of the electronic tree register. ÖNORM L 1122: 2011 replaces ÖNORM L 1122: 2003. Other relevant and supplementary standards:
- ÖNORM B 2241 garden design and landscaping - work contract standard
- ÖNORM L 1050 Soil as a plant location - terms and examination methods
- ÖNORM L 1110 plants - quality requirements, sorting regulations
- ÖNORM L 1120 Garden design and landscaping - maintenance work
- ÖNORM L 1125 Requirements for a tree register
With regard to the liability of the owner of the tree, § 1319 ABGB is used by analogy in the event of damage if the owner disregards due diligence (see the regulations in ÖNORM L 1122: 2011) or cannot prove compliance with due diligence ( e.g. no written documentation - tree cadastre in connection with the reversal of the burden of proof according to § 1298 ABGB).
Web links
- Online tree register of Vienna (viewed on March 22, 2017)
- Online tree register of Merano (viewed on May 26, 2018)