Vocational School (Switzerland)
The vocational schools provide theoretical lessons as part of the dual basic vocational training ( apprenticeship ). Often, departments for higher vocational training and / or professional training are attached to them.
The term vocational school replaced the traditional term vocational school on January 1, 2004 . The vernacular also speaks of trade school (for commercial vocational school ) and KV school (for commercial vocational school ).
The occupational fields in Switzerland , according to which the vocational schools are divided, are divided into different subject areas. The cantons must ensure that the apprentices (apprentices) can attend the scheduled lessons, be it by running vocational schools for the respective occupational field, or by sending them to a school in another canton and compensating it for this.
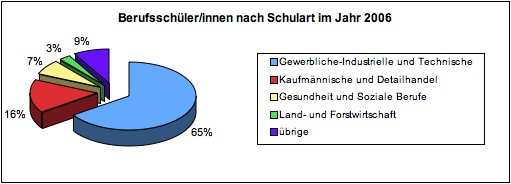
Commercial, industrial and technical professions
z. B. Hairdresser, painter, gardener, automation technician, draftsman, agricultural machinery mechanic, carpenter, geomatician, metal construction engineer
For 1-2 days a week, the learners attend the vocational school where they attend general education (including sports) and vocational classes.
general education
General education classes usually last half a day per week and cover language and communication, law and society, and sport. The goal is u. a. the improvement of social skills.
The general education curriculum is the same for all professions. Nevertheless, the lessons take place in occupational-related classes.
Vocational education
These subjects have a very close practical relevance to what has been learned in the company (e.g. professional studies, technical calculation, merchandise knowledge, materials technology, etc.).
additional
For young people with above-average talent there is the possibility of additionally attending the vocational school or of taking advantage of various optional courses . These are offered at the various vocational schools. The courses can be individually related to the profession or geared towards general education, e.g. B. IT courses or foreign language. For underperforming young people, so-called support courses are offered at the various vocational schools , which offer help for the learners.
Depending on the profession, additional training courses are also carried out. For the respective occupations, various basic requirements must also be met and various requirement profiles must be set.
Commercial vocational schools and retail trade
Most important occupations: merchant (formerly: commercial clerk), retail clerk, bookseller
When it comes to the profession of a businessman, trainees have a choice of three requirement profiles, depending on their school and personal requirements as well as their interests: basic education (B), extended basic education (E) and apprenticeship with vocational baccalaureate (M). A profile change is possible up to the beginning of the 2nd year of training.
School education
The basic school education, which mostly takes place 2 days a week, consists of the following elements:
- IKA: instruction in information, communication and administration.
- W&G: Lessons in business and society
- Languages: Lessons in German and, depending on the profile, in one or two foreign languages
- Physical education
In profile M, there are additional classes in mathematics and history and W&G is divided into finance and accounting (FRW) and economics, business administration and law (VBR).
In the third year of apprenticeship, trainees in Profiles B and E attend vocational school only one day a week, while those in Profile M attend two days a week in all years of apprenticeship.
The schools also offer the apprentices optional subjects. In some cases, language courses in England and France are also offered.
A special feature: in German-speaking Switzerland, the commercial vocational schools are usually run by the regional commercial associations. The other schools are largely funded by the cantons.
Health and Social Professions
Most important professions: Specialist care (FaBe), specialist in health (FaGe)
The training period at the vocational school after compulsory schooling is 3 years. For adults there is the possibility to complete a shortened apprenticeship of 2 years.
In the FaGe area there are various options for school education. Depending on the vocational school, the lessons are carried out in modules (block courses) or 1.5 days a week (1 day of professional studies, ½ day of general education and sports). At some schools, the school days are also coordinated with the years of apprenticeship:
- 1st year: 4 days / week
- 2nd year: 2 days / week
- 3rd year: 1 day / week
general education
The subjects of gymnastics / sport and general education are taught in schools according to their own curriculum.
Vocational education of the FaBe
Professional studies are divided into:
General professional knowledge;
- Support and care in everyday life,
- Communication and collaboration,
- People and development,
- Ethics, professional role, quality and organization
and specific professional knowledge;
- Handicapped care
- Childcare.
Vocational training at FaGe
- Care and support
- Living environment and everyday life
- Administration and logistics
- Medical technology
- Interdisciplinary professional knowledge
Additional optional courses are also offered. The apprentices also have the opportunity to complete the vocational school leaving certificate during their training.
Agriculture and Forestry
Farmer, agricultural specialty
The training to become a farmer is traditionally divided into 2 parts:
- Part: One day per week at vocational school (duration 2 years) with subsequent final apprenticeship examination 1 (LAP 1).
- Part: Agricultural School. A passed LAP1 is a condition for admission.
There are 2 ways of completing the agricultural school - either as an annual agricultural school or as a winter agricultural school with subsequent LAP2. If they pass, the graduates receive the federal certificate of proficiency.
General knowledge
In general education, sport, society, language and communication are taught.
Subject teaching
The specialist course includes:
- Crop production: general crop production, alpine and mountain agriculture and options
- Animal husbandry: general and choices
- Agricultural engineering and workshop
- Business administration
Allocation of learners to the various departments
In all professions, the school area is part of the qualification process. If they pass the examination, the apprentices receive a federal certificate of proficiency (EFZ) or the federal professional certificate (EBA).
Web links
- Framework curriculum for general education (PDF file; 94 kB)
- List of vocational schools (PDF file)
- Page no longer available , search in web archives: List of schools (PDF file)
- More detailed representation (PDF file; 318 kB)
- Educational plan FaBe (PDF file)
- Educational plan FaGe (PDF file)