Esophageal swallow
An esophageal swallow , colloquially for esophagography , is used to visualize the esophagus and the junction between the esophagus and the stomach (esophagogastric junction) using X-rays and an oral contrast agent containing barium or iodine (abbreviated CM).
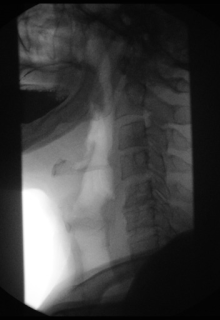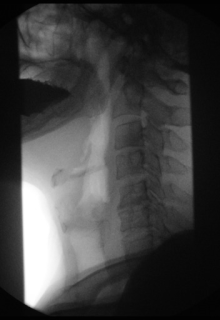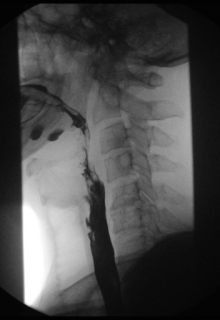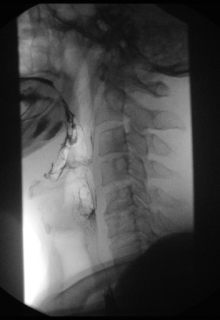
Contrast medium x-rays of the esophagus ( esophagograms ) and of the esophagogastric junction enable tumor , ulcer , fistula and diverticulum imaging as well as an assessment of the swallowing act, particularly with regard to neurogenic or muscular functional swallowing disorders.
The method is unsuitable for the detection or exclusion of esophagogastric reflux .
Use for swallowing disorders (dysphagia)
In the case of dysphagia , the functional swallowing process is examined, showing the oral, pharyngeal and oesophageal phases in two planes (lateral, anterior-posterior). Because of the high speed of the swallowing process, recording is made on film (X-ray cinematography) or digitally using digital spot imaging or recording on video tapes in order to be able to view the swallowing process later in slow motion or individual images. The advantage of film recording lies in a significantly higher local resolution of up to 200 frames / s. 25–50 frames / s are available for digital and video recordings. Contrast media of different consistencies up to solids ("barium biscuits", "barium gelatine balls") are used to simulate the function of food intake (liquid-solid). The ability to keep the food in the mouth (e.g. premature, uncontrolled draining?), The movement of the tongue , soft palate and lower jaw at the beginning of the act of swallowing, when swallowing is initiated, are assessed. Next then, the course of the throat (swallowing one-sided?) With special reference to the pharyngo- laryngeal segment (penetration into the larynx, or further into the airways?) And transition into the esophagus . It is also important whether residues remain in the piriformis sinus ( visible as a pool of saliva during laryngoscopy ). In the area of the esophagus, observation of the transport of contrast medium by contraction of the esophageal sections and assessment of the opening of the lower esophageal sphincter .
In an experimental setting, it has been proven that high-speed MRI enables a 3D representation of the act of swallowing, i.e. it can be carried out without exposure to radiation.
literature
- Gudrun Bartolome, Heidrun Schröter-Morasch (Ed.): Swallowing disorders -diagnostics and rehabilitation- . 4th revised edition. Urban & Fischer-Verlag, Munich 2010, ISBN 978-3-437-47161-2 .
- Pschyrembel Clinical Dictionary (Online): Esophagography .
- W. Schuster, D. Färber (editor): Children's radiology. Imaging diagnostics . Vol. II, 2nd edition, Springer 1996, ISBN 3-540-60224-0 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ S3 guideline Gastroesophageal reflux disease - results of "evidence" based consensus conference of the German Society of Digestive and Metabolic Diseases. In: AWMF online (as of 2008)
- ↑ A. Olthoff, S. Zhang, F. Frahm: High-speed magnetic resonance tomography for the dynamic representation of the normal swallowing act. In: Current Phoniatric-Pedaudiological Aspects. 19, 2011, pp. 44-47.