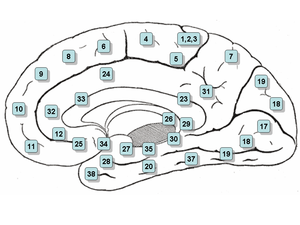
Brodmann area
Brodmann areas ( BA ) are the cerebral cortex fields of humans that are divided into fields according to cyto- and myeloarchitectonics.
The division of the Brodmann areas goes back to the German neuroanatomist and psychiatrist Korbinian Brodmann , who originally divided the cerebral cortex into 52 fields. In the meantime, however, the numbering has been further subdivided, so that, for example, Brodmann areas 23a and 23b respectively exist.
Areas that can be assigned to specific functions
| Area | Functional assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 2 3 |
Somatosensory cortex |
| 4th | Primary motor cortex |
| 5 | Posterior parietal cortex |
| 6th | Premotor cortex and supplementary motor cortex |
| 7th | Posterior parietal cortex |
| 8th | Frontal eye field |
| 17th | Primary visual cortex |
| 18 19 |
Secondary and tertiary visual cortex |
| 22nd | Wernicke area (sensory language region) |
| 23 | Part of the posterior cingular cortex |
| 24 | Part of the anterior cingular cortex |
| 25th | Subgenual cortex |
| 28 34 |
Entorhinal cortex (including olfactory sense ) |
| 37 | Fusiform gyrus |
| 39 40 |
Transition region between secondary sensory projection centers and the tertiary association area ( gyrus angularis and gyrus supramarginalis ) |
| 41 | primary auditory cortex [the primary auditory cortex (Brodmann area 41) is not visible from the "outside" in situ, but is de facto located on the transverse temporal gyri (also: Heschl transverse windings), which are part of the temporal lobe within the sulcus lateralis] |
| 42 | secondary auditory cortex |
| 43 | Subcentral area |
| 44 45 |
Broca area (motor language region) |
| 46 | dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
literature
- Korbinian Brodmann : Comparative localization theory of the cerebral cortex. Shown in its principles on the basis of the cell structure. Johann Ambrosius Barth Verlag, Leipzig 1909 (2nd unchanged edition. Ibid. 1925; reprint of the original edition from 1909, with an afterword and a bibliography by Ernst Winkelmann and Karl Seidel. Ibid. 1985, ISBN 3-335-00010-2 ).
Web links
Commons : Brodmann areas - album with pictures, videos and audio files
- Roche - Lexicon of Medicine. 5th edition. Urban and Fischer, Munich 2003, ISBN 3-437-15072-3 .
Individual evidence
- ^ S. Gauggel, M. Herrmann: Handbook of Neuro- and Biopsychology. Hogrefe, Göttingen u. a. 2008, ISBN 978-3-8017-1910-4 , p. 260.
- ↑ Peter Duus: Neurological-topical diagnostics. Anatomy, physiology, clinic. 5th revised edition. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart a. a. 1990, ISBN 3-13-535805-4 , p. 389.
- ^ S. Gauggel, M. Herrmann: Handbook of Neuro- and Biopsychology. Hogrefe, Göttingen u. a. 2008, ISBN 978-3-8017-1910-4 , p. 258.