Condylomata gigantea
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| A 63.0 | Genital warts |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
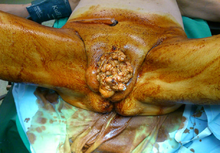
As condylomata gigantea or Buschke-Lowenstein tumor a rare chronic form is infection with human papillomavirus designated (HPV), the first time in 1925 by Abraham Buschke and Ludwig Lowenstein described (1885-1959). This results in large, rapidly growing, cauliflower-like tumors mostly in the genital area, less often in the perianal region. The tumor has a high local malignancy tendency, but without the potential to form metastases . Since the tumors hardly respond to conservative measures, the therapy consists of a surgical removal of the tumor with subsequent removal of the base of the wart using a laser . However, the recurrence rate is very high.
The cause of the development of a Buschke-Löwenstein tumor are long-term persistent HPV infections , which via genital warts ( condylomata acuminata ) ultimately lead to verrucous (wart-like) carcinoma . In particular, the low risk types HPV 6, HPV 11, and HPV 56 are responsible for the disease.
The German Dermatological Society and the German Society for Coloproctology differentiate between condylomata gigantea and Buschke-Löwenstein tumor. The destructive (destructive) form is known as the Buschke-Löwenstein tumor and the non-destructive form as the condylomata gigantea.
literature
- JM Martin, I. Molina et al. a .: Buschke-Lowenstein tumor. In: Journal of dermatological case reports. Volume 2, number 4, December 2008, pp. 60-62, doi: 10.3315 / jdcr.2008.1019 , PMID 21886716 , PMC 3157782 (free full text).
- A. Frega, P. Stentella, et al. a .: Giant condyloma acuminatum or buschke-Lowenstein tumor: review of the literature and report of three cases treated by CO2 laser surgery. A long-term follow-up. In: Anticancer Research . Volume 22, Number 2B, 2002 Mar-Apr, pp. 1201-1204, PMID 12168925 (Review).
Individual evidence
- ↑ A. Buschke, L. Löwenstein: About carcinoma-like condylomata acuminata of the penis. In: Berl Klin Wschr. Volume 4, 1925, pp. 1726-1728.
- ^ C. Steffen: The men behind the eponym - Abraham Buschke and Ludwig Lowenstein: giant condyloma (Buschke-Loewenstein). In: The American Journal of dermatopathology. Volume 28, Number 6, December 2006, pp. 526-536, doi: 10.1097 / 01.dad.0000211528.87928.a8 , PMID 17122499 .
- ↑ Santos, Liliana et al .: Buschke-Löwenstein tumor, A case in a patient coinfected with Human immunodeficiency virus and Human papillomavirus . In: Next Document GE J Port Gastrenterol . tape 19 , 2012, p. 199-203 ( abstract ).
- ↑ Jose M Martin et al .: Buschke-Lowenstein tumor . In: J Dermatol Case Rep . tape 2 , no. 4 , December 27, 2008, p. 60-62 , doi : 10.3315 / jdcr.2008.1019 .
- ↑ Gong-Yau Chu et al .: Buschke-Löwenstein tumor (giant condyloma acuminatum) successfully treated by topical photodynamic therapy: a case report . In: Dermatologica Sinica . tape 31 , no. 2 , June 2013, p. 94-97 , doi : 10.1016 / j.dsi.2012.08.003 .
- ^ Peter Altmeyer : Condylomata gigantea. enzyklopaedie-dermatologie.de, accessed on December 24, 2016
- ↑ Genital warts. Guidelines of the German Dermatological Society and the German Society for Coloproctology, AWMF Guideline Register No. 013/008, development stage 1