Chlorates


Chlorates are salts of the chloric acid HClO 3 . They contain the chlorate ion (ClO 3 - ) as an anion . Chlorine has an oxidation number of +5. Important chlorates are sodium chlorate , aluminum chlorate and potassium chlorate .
Most chlorates are strong and spontaneously reacting oxidants . Mixtures of chlorates with reducing agents used to be used as explosives and detonating agents (see chlorate explosives ). Today they are no longer used because of their sensitivity to friction and the tendency to spontaneous reactions.
Sodium and potassium chlorate have been used as weed killers in the past . The maximum residue levels in food / products are regulated by a regulation (EU) .
Bond structure
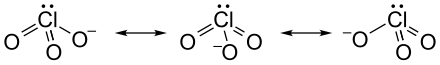
The Lewis notation usually only shows a mesomeric boundary structure of the chlorate ion. In fact, all Cl-O bonds are identical, which is expressed by the same length of all bonds (for potassium chlorate for example 1.49 Å)
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Brockhaus ABC chemistry. VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 242.
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 1: A-Cl. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1979, ISBN 3-440-04511-0 , p. 714.
- ↑ The entry of chlorate into the food chain should be reduced. Federal Institute for Risk Assessment, accessed on June 23, 2020 .
- ↑ COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2020/749. June 4, 2020, accessed June 23, 2020 .
- ↑ J. Danielsen, A. Hazell, FK Larsen: The structure of potassium chlorate at 77 and 298 K . In: Acta Cryst. . B37, 1981, pp. 913-915. doi : 10.1107 / S0567740881004573 .